 67 citations,
January 2020 in “Cellular & Molecular Immunology/Cellular & molecular immunology”
67 citations,
January 2020 in “Cellular & Molecular Immunology/Cellular & molecular immunology” Tissue-resident memory T cells can protect against infections and cancer but may also contribute to autoimmune diseases.
51 citations,
August 2013 in “The Journal of experimental medicine/The journal of experimental medicine” Loss of a specific protein in skin cells causes symptoms similar to psoriasis.
 32 citations,
April 1994 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
32 citations,
April 1994 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” High androgen levels and genetic factors likely cause Becker's nevus and related symptoms.
 27 citations,
October 1999 in “Experimental and Molecular Pathology”
27 citations,
October 1999 in “Experimental and Molecular Pathology” Stump-tailed macaque best for researching hair loss causes and treatments.
20 citations,
August 2005 in “The Journal of laboratory and clinical medicine” Mice with damaged skin or hair follicles are more susceptible to anthrax infection.
15 citations,
March 2000 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” As skin cells mature, vitamin D receptor levels decrease while retinoid X receptor α levels increase.
 7 citations,
September 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
7 citations,
September 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” IL-36α helps grow new hair follicles and speeds up wound healing.
 December 2024 in “Pharmaceutics”
December 2024 in “Pharmaceutics” Extracellular vesicles show promise for treating psoriasis by reducing inflammation and skin lesions.

Psoriasis is linked to a higher risk of autoimmune diseases and other health conditions.

People with psoriasis have more health problems, including autoimmune diseases, than those without it.
 1308 citations,
March 1998 in “Journal of bone and mineral research”
1308 citations,
March 1998 in “Journal of bone and mineral research” The vitamin D receptor is crucial for bone health and affects various body systems, with mutations potentially leading to disease.
131 citations,
November 2010 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Cyclosporine is effective for skin conditions but has declined in use due to toxicity concerns.
111 citations,
August 1998 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” μ-opiate receptors in skin cells may affect skin health and healing.
93 citations,
May 2002 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Overexpressing thrombospondin-1 in mice skin prevents UVB-induced skin damage.
78 citations,
November 2005 in “Endocrinology” Hairless protein can block vitamin D activation in skin cells.
65 citations,
August 2013 in “Acta Biomaterialia” The new matrix improves skin regeneration and graft performance.
 42 citations,
May 2016 in “Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology”
42 citations,
May 2016 in “Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology” Fat cells are important for tissue repair and stem cell support in various body parts.
 26 citations,
October 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
26 citations,
October 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” The secretome from mesenchymal stem cells shows promise for treating skin conditions and improving skin and hair health, but more research is needed.
 23 citations,
December 2021 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
23 citations,
December 2021 in “Frontiers in Immunology” IL-1 family cytokines are crucial for skin defense and healing, but their imbalance can cause skin diseases.
 16 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
16 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A 10-year-old girl with Fox Fordyce disease improved with treatment, suggesting the disease can occur before puberty and might be underdiagnosed in young girls.
 12 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
12 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Fox Fordyce disease might be more common in prepubertal girls than thought and can be managed with treatment.
 11 citations,
January 2000 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
11 citations,
January 2000 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Short telomeres contribute to aging and cancer, and while telomerase can delay aging, it may also promote cancer.
11 citations,
November 1998 in “Journal of dermatological science” Knocking out certain genes in mice helps understand skin and hair growth problems.
 9 citations,
July 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology”
9 citations,
July 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology” Topical L-thyroxine may help with wound healing and hair growth but should be used short-term due to potential risks.
 9 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
9 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Fox Fordyce disease can occur in prepubertal girls and may be underdiagnosed.
 8 citations,
July 2022 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
8 citations,
July 2022 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Skin cells release substances important for healing and fighting infection, and understanding these could improve skin disorder treatments.
7 citations,
May 2012 in “Journal of veterinary diagnostic investigation” Some young Angus cattle had skin problems due to not enough vitamin A, which got better after they were given more vitamin A.
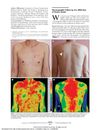 6 citations,
September 2010 in “Archives of Dermatology”
6 citations,
September 2010 in “Archives of Dermatology” Thermography matched the patient's pain levels in a shingles case and might help diagnose shingles without a rash.
March 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Mitochondrial dysfunction is linked to various skin conditions and could be a target for treatments.

New insights into cell communication in psoriasis suggest innovative drug treatments.



















