 25 citations,
April 2008 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
25 citations,
April 2008 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Encapsulated human hair cells can substitute for natural hair cells to grow hair.
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” A new tool helps study hair follicle cells to develop better treatments for hair disorders.
 75 citations,
March 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
75 citations,
March 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Aging mice have slower hair regeneration due to changes in signal balance, but the environment, not stem cell loss, controls this, suggesting treatments could focus on environmental factors.
2 citations,
November 2023 in “Biomolecules” WNT signaling is crucial for skin development and healing.
53 citations,
September 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair follicle cells help protect against immune attacks by regulating T-cell activity.
194 citations,
November 2006 in “Science” A genetic mutation in the LIPH gene causes hair loss and growth defects.
 29 citations,
December 2005 in “BioEssays”
29 citations,
December 2005 in “BioEssays” Wnt/ß-catenin signaling is crucial for regulating skin stem cells and hair growth, with the right levels and timing needed for proper function.
 18 citations,
October 2021 in “Frontiers in Physiology”
18 citations,
October 2021 in “Frontiers in Physiology” Lipocalin-Type Prostaglandin D2 Synthase (L-PGDS) is a protein that plays many roles in the body, including sleep regulation, pain management, food intake, and protection against harmful substances. It also affects fat metabolism, glucose intolerance, cell maturation, and is involved in various diseases like diabetes, cancer, and arthritis. It can influence sex organ development and embryonic cell differentiation, and its levels can be used as a diagnostic marker for certain conditions.
 8 citations,
November 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
8 citations,
November 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Certain genes are more active in baby scalp cells and can help grow hair when added to adult mouse skin cells.
 15 citations,
January 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
15 citations,
January 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” Lanyu pigs show that partial-thickness wounds can partially regenerate important skin structures, which may help improve human skin healing.
 13 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine”
13 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine” The workshop discussed the role of a protein called calreticulin in health and disease, its potential as a treatment target, and its possible use as a disease marker.
MicroRNA miR-22 causes hair loss by making hair follicles regress early.
 5 citations,
April 2022 in “Journal of Ethnopharmacology”
5 citations,
April 2022 in “Journal of Ethnopharmacology” Chinese herbal medicine can help treat hair loss by promoting hair growth and preventing cell death, maintaining a balance between hair growth and loss.
 6 citations,
October 2000 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
6 citations,
October 2000 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Preventing hair loss is more effective than regrowth; oral finasteride is a realistic option.
 520 citations,
February 2001 in “Journal of Clinical Investigation”
520 citations,
February 2001 in “Journal of Clinical Investigation” VEGF helps hair grow and determines follicle size by increasing blood vessel growth.
 5 citations,
February 2016 in “Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers”
5 citations,
February 2016 in “Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers” Hair loss is significantly linked to lower levels of certain genes in hair follicles.
 1 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” SM04554 may increase hair growth as a topical treatment for androgenetic alopecia.
 1 citations,
August 1994 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
1 citations,
August 1994 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Hair loss happens due to faster cell growth and fewer cells in affected follicles.
 16 citations,
July 2013 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
16 citations,
July 2013 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Pigmented casts are common in several hair loss conditions and can help diagnose specific types of alopecia.
 127 citations,
December 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
127 citations,
December 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Mice hair growth patterns get more complex with age and can change with events like pregnancy or injury.
 2 citations,
May 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
2 citations,
May 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Sebaceous glands can heal and regenerate after injury using their own stem cells and help from hair follicle cells.
 51 citations,
July 2010 in “Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism”
51 citations,
July 2010 in “Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism” Prolactin may play a significant role in skin and hair health and could be a target for treating skin and hair disorders.
 57 citations,
February 1994 in “Experimental dermatology”
57 citations,
February 1994 in “Experimental dermatology” Melatonin affects mouse skin and may regulate skin functions.
 1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology” Hair loss, known as Androgenetic Alopecia, is often caused by hormones and can be diagnosed using noninvasive techniques. Treatments include topical minoxidil and oral finasteride, with new treatments being explored. There may also be a link between this type of hair loss and heart disease risk.
 October 2024 in “Small Methods”
October 2024 in “Small Methods” Platinum nanozyme microneedles can effectively and safely promote hair growth for androgenetic alopecia.
 29 citations,
September 2014 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology”
29 citations,
September 2014 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology” Horizontal sections of scalp biopsies are good for diagnosing Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia and help customize treatment.
 49 citations,
September 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
49 citations,
September 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The study found that bioengineered hair follicles work when using cells from the same species but have issues when combining human and mouse cells.
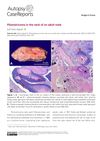 January 2022 in “Autopsy and Case Reports”
January 2022 in “Autopsy and Case Reports” A man had a non-cancerous neck tumor related to hair follicles removed with no return of the tumor.
December 2024 in “Biomedicines” Rat hair follicle stem cells may help heal skin wounds.
 122 citations,
April 1995 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
122 citations,
April 1995 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” The document describes how to tell different types of non-scarring hair loss apart by looking at hair and scalp tissue under a microscope.
























