 July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Lichen Planopilaris is a hair loss condition best treated early with various medications, including hydroxychloroquine, to prevent permanent baldness.
 20 citations,
August 2018 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
20 citations,
August 2018 in “Clinics in Dermatology” The conclusion is that understanding and addressing the psychological effects of alopecia areata is important for effective treatment.
5 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” Frontal fibrosing alopecia might be linked to autoimmune diseases.
143 citations,
January 2004 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease causing hair loss, treatable with immune-modulating drugs, and linked to genetics.
7 citations,
January 2017 in “Neuromuscular Disorders” A rare autoimmune condition, Satoyoshi syndrome, can start in adults and improve with immunosuppressive treatment.
 50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Alopecia Areata has no guaranteed treatment for hair regrowth, but options like corticosteroids and minoxidil are used, with future research focusing on genetic and immune therapies.
162 citations,
October 2014 in “Autoimmunity reviews” Alopecia areata is caused by the immune system attacking hair follicles.
 July 2022 in “medRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
July 2022 in “medRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Satoyoshi syndrome is likely an autoimmune disease that mainly affects young women and improves with immune-related treatments.
 122 citations,
November 1984 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
122 citations,
November 1984 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” No single treatment is consistently effective for alopecia areata, and more research is needed.
 3 citations,
October 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
3 citations,
October 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Trichoscopy helps tell apart Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia and Lichen planopilaris by showing different hair and scalp features.
 1 citations,
August 2021 in “Movement disorders clinical practice”
1 citations,
August 2021 in “Movement disorders clinical practice” A man with Isaac's syndrome affecting only one side of his body improved after immune system-targeted treatment.
 July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is a type of hair loss affecting mostly older women, with no agreed best treatment.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with no cure, but various treatments exist that require personalized approaches.
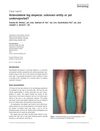 September 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
September 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Anterolateral leg alopecia is a benign, nonprogressive hair loss condition on the lower legs that is not well understood and may resolve on its own.
 10 citations,
March 2014 in “Scandinavian journal of clinical and laboratory investigation”
10 citations,
March 2014 in “Scandinavian journal of clinical and laboratory investigation” Malondialdehyde-modified DNA may trigger an immune response in alopecia areata patients.
 4 citations,
August 2013 in “Case reports in dermatology”
4 citations,
August 2013 in “Case reports in dermatology” A patient with total hair loss developed vitiligo after using a treatment called DCP.
14 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Inflammation Research” Alopecia areata patients, especially women with nail issues or atopic diseases, are at higher risk for other autoimmune diseases.
 March 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
March 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” A girl with severe hair loss saw hair regrowth after using cannabis.
 43 citations,
June 2018 in “Clinics in dermatology”
43 citations,
June 2018 in “Clinics in dermatology” People with atopic dermatitis are more likely to develop other skin conditions due to shared genetics and immune pathways.
 1 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” A woman on immunosuppressants developed two rare scalp conditions, which improved with specific treatments.
 May 2020 in “International journal of biology, pharmacy and allied sciences”
May 2020 in “International journal of biology, pharmacy and allied sciences” Vitiligo is often found with other autoimmune diseases, which is important to know to help patients.
 8 citations,
October 2019 in “Immunological investigations”
8 citations,
October 2019 in “Immunological investigations” The AIRE gene variant rs2075876 is linked to a higher risk of alopecia areata in males.
8 citations,
October 2014 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Patients with alopecia areata should be checked for muscle spasms, diarrhea, and ANA to avoid missing Satoyoshi syndrome.
 7 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
7 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Two siblings both had a rare case of alopecia areata at the same time.
 15 citations,
April 2003 in “Journal of dermatology”
15 citations,
April 2003 in “Journal of dermatology” Alopecia areata causes hair loss due to an immune attack on hair follicles, influenced by genetics and environment.
 2 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal of Pigmentary Disorders”
2 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal of Pigmentary Disorders” Vitiligo causes white skin patches and can lead to psychological stress.
 2 citations,
January 2019
2 citations,
January 2019 The document concludes that autoimmune skin disorders are treated with corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs.
 3 citations,
August 2022 in “Curēus”
3 citations,
August 2022 in “Curēus” The SARS-CoV-2 vaccine may be linked to triggering autoimmune conditions like Alopecia Areata.
 38 citations,
October 2006 in “Fertility and Sterility”
38 citations,
October 2006 in “Fertility and Sterility” The document concludes that identifying the cause of amenorrhea is crucial for proper treatment.
1 citations,
November 2016 in “Frontiers in neurology” Steroid treatment improved both gut and nerve symptoms in a man with Cronkhite–Canada syndrome.























