 1 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of stem cell research and medicine”
1 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of stem cell research and medicine” Fat-derived stem cell therapies can potentially increase hair growth and thickness in people with hair loss.
 August 2023 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
August 2023 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” Using adipose-derived stem cell media with minoxidil may help regrow hair in men with hair loss.
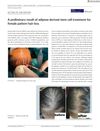 April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Stem cell treatment improved hair density in female hair loss patient.
October 2021 in “Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open” Adipose-derived stem cells may help treat hair loss.
 13 citations,
January 2018 in “Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry”
13 citations,
January 2018 in “Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry” Fat-derived stem cells can help protect and repair skin stem cells from aging caused by UV light.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of clinical & experimental dermatology research”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of clinical & experimental dermatology research” Both fat-derived stem cells and platelet-rich plasma are effective and safe for hair loss, but stem cells give better results with more side effects.
April 2018 in “Cytotherapy” Both treatments promote hair growth safely, but stem cells are slightly more effective.
 1 citations,
February 2022 in “Experimental Dermatology”
1 citations,
February 2022 in “Experimental Dermatology” Certain proteins are found at higher levels in balding areas compared to non-balding areas, suggesting a link to hair loss. This could be useful for diagnosing and treating hair loss.
21 citations,
August 2017 in “Journal of veterinary internal medicine” Combining amino acid and stem cell therapy may help manage hepatocutaneous syndrome in dogs.
 76 citations,
January 2017 in “World Journal of Stem Cells”
76 citations,
January 2017 in “World Journal of Stem Cells” Fat tissue cells are a promising option for healing various diseases, but more research is needed to ensure they are safe and effective.
 55 citations,
May 2017 in “Current stem cell research & therapy”
55 citations,
May 2017 in “Current stem cell research & therapy” Using fat-derived stem cells for hair loss treatment is safe and effective, improving hair growth and patient satisfaction.
 28 citations,
December 2012 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery”
28 citations,
December 2012 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery” Proteins from stem cells improved hair growth in patients with hair loss.
 30 citations,
June 2017 in “Current stem cell research & therapy”
30 citations,
June 2017 in “Current stem cell research & therapy” Adipose-derived stem cells (fat cells) show promise in treating hair loss in both men and women.
 42 citations,
February 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
42 citations,
February 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Minoxidil boosts hair growth by triggering growth factor release from specific stem cells.
 17 citations,
July 2014 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy”
17 citations,
July 2014 in “Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy” The new method for isolating stem cells from fat is simple and effective, producing cells that grow faster and are better for hair regeneration.
 12 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
12 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Scientists made stem cells that can grow hair by adding three specific factors to them.
 September 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
September 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Fat-derived stem cells may help treat skin aging and hair loss.
 January 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
January 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Proteins like aPKC and PDGF-AA, substances like adenosine and ATP, and adipose-derived stem cells all play important roles in hair growth and health, and could potentially be used to treat hair loss and skin conditions.
 2 citations,
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Fat tissue stem cells show promise for repairing different body tissues and are being tested in clinical trials.
 January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” Fat-derived stem cells and their secretions show promise for treating skin aging and hair loss.
 81 citations,
December 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
81 citations,
December 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Fat tissue stem cells may help increase hair growth.
 42 citations,
February 2014 in “Stem Cells and Development”
42 citations,
February 2014 in “Stem Cells and Development” Vitamin C helps adipose-derived stem cells grow and may support hair growth.
53 citations,
April 2016 in “Stem cell research & therapy” LL-37 helps stem cells grow and move, aiding tissue regeneration and hair growth.
 19 citations,
January 2017 in “Stem Cells International”
19 citations,
January 2017 in “Stem Cells International” Adipose-derived stem cells show promise in treating skin conditions like vitiligo, alopecia, and nonhealing wounds.
 5 citations,
August 2020 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
5 citations,
August 2020 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” Using fat-derived stem cells with the drug meglumine antimoniate can help control skin disease and reduce parasites in mice with leishmaniasis.

The combination of ADSC secretome and minoxidil was most effective for hair growth in people with hair loss.
 88 citations,
July 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
88 citations,
July 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Using human fat tissue derived stem cells in micrografts can safely and effectively increase hair density in people with hair loss.
 83 citations,
March 2015 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
83 citations,
March 2015 in “International Journal of Dermatology” ADSC-CM treatment improved hair density and thickness in women with hair loss, safely and effectively.
4 citations,
November 2021 in “Molecular Medicine Reports” Combining narrow-band ultraviolet B light and stem cell transplantation helps repigmentation in vitiligo by maintaining calcium balance in mice.
 4 citations,
August 2021 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
4 citations,
August 2021 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Stem cells show promise for hair loss and skin treatments in aesthetics but need more research on safety and standard methods.

























