 December 2023 in “Scientific reports”
December 2023 in “Scientific reports” Fermented soy protein may help prevent bone loss by affecting bone cell activity.
91 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” NK cells play a role in skin diseases like eczema and psoriasis.
8 citations,
June 2023 in “Journal of clinical medicine” Nanofat shows promise for facial rejuvenation and treating skin issues but needs more research for long-term safety.
 21 citations,
July 2022 in “Orphanet journal of rare diseases”
21 citations,
July 2022 in “Orphanet journal of rare diseases” New treatments for ichthyosis, like protein replacement and gene therapy, show promise and may become standard care.
6 citations,
October 2021 in “Biomedical Research and Therapy” Alopecia areata patients have higher levels of IL-6 and TNF-α.
 5 citations,
December 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
5 citations,
December 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Enzymes called PADIs play a key role in hair growth and loss.
9 citations,
June 2023 in “Cells” Certain natural and synthetic compounds may help treat inflammatory skin diseases by targeting a specific signaling pathway.
 October 2021 in “Dermatology Reports”
October 2021 in “Dermatology Reports” Higher IL-17A levels indicate more severe alopecia areata.
 12 citations,
May 2017 in “Pharmacology & therapeutics”
12 citations,
May 2017 in “Pharmacology & therapeutics” Targeting immune tolerance issues in Alopecia Areata could restore hair growth and maintain remission.
 3 citations,
July 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
3 citations,
July 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology” An elderly man's hair grew back after treatment with secukinumab, possibly due to reduced scalp inflammation or the medication's direct effects.
 January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Acne is linked to inflammation and insulin resistance, and is associated with various syndromes that require different treatments.
 6 citations,
January 2012 in “Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology”
6 citations,
January 2012 in “Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology” Ustekinumab might work for severe psoriasis, but more research is needed to be sure.
 1 citations,
January 2020 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
1 citations,
January 2020 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” Certain gene variations may increase the risk and severity of alopecia areata.
 October 2023 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
October 2023 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” PPAR-γ may be a key target for treating alopecia areata and other skin conditions.
 January 2025 in “Acta Dermato Venereologica”
January 2025 in “Acta Dermato Venereologica” Mothers with alopecia areata have a higher risk of adverse birth outcomes.
 79 citations,
March 2017 in “Dermatologic clinics”
79 citations,
March 2017 in “Dermatologic clinics” Vitiligo affects overall health and self-esteem, needing more research and awareness.
 70 citations,
February 2019 in “The journal of immunology/The Journal of immunology”
70 citations,
February 2019 in “The journal of immunology/The Journal of immunology” Short-chain fatty acids from *Cutibacterium acnes* cause skin inflammation, contributing to acne.
 13 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology”
13 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology” 308-nm excimer light therapy helped over a third of treatment-resistant alopecia universalis patients regrow most of their hair.
 January 2022 in “Medical research archives”
January 2022 in “Medical research archives” Taking vitamin D might improve life for MS patients and reduce skin side effects from alemtuzumab treatment.
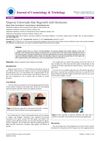 January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology”
January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology” A man with severe hair loss regrew hair after hormone treatment.
 77 citations,
June 2017 in “Advances in Therapy”
77 citations,
June 2017 in “Advances in Therapy” New treatments for Alopecia Areata, like JAK inhibitors, show promise for hair regrowth and are likely to change future treatment approaches.
 13 citations,
January 2022 in “Advances in Dermatology and Allergology”
13 citations,
January 2022 in “Advances in Dermatology and Allergology” Alopecia areata may be linked to imbalanced gut bacteria.
 5 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology”
5 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” Environmental factors like diet and vitamin levels, especially Vitamin D, can affect autoimmune diseases differently, with lifestyle changes potentially improving outcomes.
 April 2023 in “Medizinische Genetik”
April 2023 in “Medizinische Genetik” New research has found 14 genes linked to the risk of developing alopecia areata, improving understanding and treatment options.
 3 citations,
November 2021 in “World Journal of Clinical Pediatrics”
3 citations,
November 2021 in “World Journal of Clinical Pediatrics” Vitamin D might help treat some types of hair loss, but more research is needed.
1 citations,
January 2018 in “Skin appendage disorders” The complement system might be involved in the development of alopecia areata and could lead to new treatments.
1 citations,
August 2023 in “Biomolecules” Certain immune-related proteins are higher in people with alopecia and their healthy relatives, hinting at a genetic link.
March 2024 in “Nutrients” Alopecia Areata is linked to specific gut bacteria and metabolites, indicating a complex gut microbiome.
 May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” New understanding and treatments for hair loss are improving, but more research is needed.
 March 2022 in “Wound practice & research”
March 2022 in “Wound practice & research” New treatments for alopecia areata show promise, but standardized guidelines are needed.























