 April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The Engrailed-1 gene plays a key role in the development of sweat glands in mice.
11 citations,
January 1977 in “Archives of dermatological research” Mouse tail skin has different keratinization near hair follicles and scales.
 13 citations,
June 2020 in “Scientific reports”
13 citations,
June 2020 in “Scientific reports” Melatonin stimulates the skin components of ram's scrotum during their non-breeding season.
 9 citations,
January 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks”
9 citations,
January 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks” Skin's epithelial stem cells are crucial for repair and maintenance, and understanding them could improve treatments for skin problems.
 32 citations,
April 2014 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
32 citations,
April 2014 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Loss of keratin K2 causes skin problems and inflammation.
 44 citations,
December 1991 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences”
44 citations,
December 1991 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences” EGF and FGF help hair growth by affecting cell differentiation and fiber growth.
39 citations,
November 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Fatp4 is crucial for healthy skin development and function.
 5 citations,
July 2022 in “Orphanet journal of rare diseases”
5 citations,
July 2022 in “Orphanet journal of rare diseases” RSPO1 mutations in certain patients lead to skin cells that don't develop properly and are more likely to become invasive, increasing the risk of skin cancer.
45 citations,
December 2007 in “The FASEB journal” There are two types of stem cells in rodent hair follicles, each with different keratin proteins.
22 citations,
August 2020 in “Cells” TGM3 is important for skin and hair structure and may help diagnose cancer.
 53 citations,
September 1999 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology”
53 citations,
September 1999 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology” K16 can partially replace K14 but causes hair loss and skin issues.
 46 citations,
November 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
46 citations,
November 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The vitamin D receptor is essential for skin stem cells to grow, move, and become different cell types needed for skin healing.
 1 citations,
March 1954 in “Archives of dermatology”
1 citations,
March 1954 in “Archives of dermatology” Animal research has greatly advanced dermatology.
 96 citations,
June 2017 in “Nature Communications”
96 citations,
June 2017 in “Nature Communications” A WNT10A gene mutation leads to ectodermal dysplasia by disrupting cell growth and differentiation.
 54 citations,
November 2015 in “Methods in enzymology on CD-ROM/Methods in enzymology”
54 citations,
November 2015 in “Methods in enzymology on CD-ROM/Methods in enzymology” Keratins are important for skin cell health and their problems can cause diseases.
 38 citations,
January 2006 in “Journal of Cellular Biochemistry”
38 citations,
January 2006 in “Journal of Cellular Biochemistry” Researchers isolated a new type of stem cell from mouse skin that can renew itself and turn into multiple cell types.
92 citations,
April 1999 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Nonpalmoplantar skin cells can be made to express keratin 9 by interacting with palmoplantar fibroblasts.
 6 citations,
November 2022 in “Development”
6 citations,
November 2022 in “Development” New research shows that skin diversity is influenced by different types of dermal fibroblasts and their development, especially involving the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
4 citations,
June 2023 in “Journal of developmental biology” The skin systems of jawed vertebrates evolved diverse appendages like hair and scales from a common structure over 420 million years ago.
 January 2023 in “Indian dermatology online journal”
January 2023 in “Indian dermatology online journal” A boy with Pachyonychia congenita has a confirmed gene mutation, highlighting the need for a local genetic database in India.
 August 2022 in “Metabolites”
August 2022 in “Metabolites” Different types of skin on mice have unique chemical profiles related to how they grow and react to stress.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” The document explains what healthy skin, nails, and hair look like on an ultrasound.
 26 citations,
May 2014 in “BioEssays”
26 citations,
May 2014 in “BioEssays” Using neurohormones to control keratin can lead to new skin disease treatments.
 2 citations,
July 2021 in “Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications”
2 citations,
July 2021 in “Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications” CTHRC1 helps hair grow back, and plantar dermis mixture boosts it.
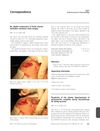 2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Chemotherapy improved a girl's painful foot condition linked to pachyonychia congenita.
124 citations,
July 2017 in “eLife” Type XVII collagen helps control skin cell growth and could be a target for anti-aging treatments.
 November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Skin cells and certain hair follicle areas produce hemoglobin, which may help protect against oxidative stress like UV damage.
Type XVII collagen helps control skin cell growth and may have anti-aging effects.
Type XVII collagen may help prevent skin aging.
3 citations,
February 2015 in “Mechanisms of development” Hormones and stretching both needed for nipple area skin growth in mice.




















