 47 citations,
July 2014 in “European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics”
47 citations,
July 2014 in “European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics” Scientists created a gel with nanoparticles to deliver medicine to hair follicles effectively.
 8 citations,
April 2010 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
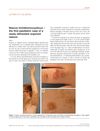
8 citations,
April 2010 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The first pediatric case of naevus trichilemmocysticus was documented.
[object Object] 5 citations,
January 2021 in “Frontiers in cell and developmental biology” Skin cysts might help advance stem cell treatments to repair skin.
 4 citations,
July 2022 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
4 citations,
July 2022 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” The document concludes that understanding adult stem cells and their environments can help improve skin regeneration in the future.
 3 citations,
June 2023 in “Advanced Materials”
3 citations,
June 2023 in “Advanced Materials” The new dressing speeds up burn wound healing and improves recovery compared to a commercial dressing.
 2 citations,
December 2022 in “Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology”
2 citations,
December 2022 in “Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology” Organoids created from stem cells are used to model diseases, test drugs, and develop personalized and regenerative medicine.
 1 citations,
July 2021 in “Organoid (Online)”
1 citations,
July 2021 in “Organoid (Online)” Organoid technology is advancing and entering commercial use, with applications in disease modeling, drug development, and personalized medicine.
January 2025 in “Burns & Trauma” Skin organoids help improve wound healing and tissue repair.
 December 2024 in “Medical Review”
December 2024 in “Medical Review” Organoids help study and treat genetic diseases, offering personalized medicine and therapy testing.
 202 citations,
June 2005 in “Aaps Pharmscitech”
202 citations,
June 2005 in “Aaps Pharmscitech” Lecithin organogels could be good for applying drugs to the skin because they are stable, safe, and can improve drug absorption.
67 citations,
June 2019 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences” A new 3D culture system helps grow and study mouse skin stem cells for a long time.
 31 citations,
January 2021 in “Experimental Dermatology”
31 citations,
January 2021 in “Experimental Dermatology” Skin organoids are a promising new model for studying human skin development and testing treatments.
 26 citations,
January 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
26 citations,
January 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” Researchers created early-stage hair-like structures from skin cells, showing how these cells can self-organize, but more is needed for complete hair growth.
20 citations,
November 2021 in “Frontiers in cell and developmental biology” Skin organoids from stem cells could better mimic real skin but face challenges.
14 citations,
June 2022 in “Stem cell reports” The study created hair-bearing skin models that lack a key protein for skin layer attachment, limiting their use for certain skin disease research.
 4 citations,
July 2022 in “Annals of translational medicine”
4 citations,
July 2022 in “Annals of translational medicine” Scientists created complete hair-like structures by growing mouse skin cells together in a special gel.
 1 citations,
September 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
1 citations,
September 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Skin organoids from stem cells can help study and treat skin issues but face some challenges.
 November 2024 in “Experimental Dermatology”
November 2024 in “Experimental Dermatology” SKO-derived SKP-like cells may help with hair regeneration and skin restoration.
 January 2024 in “Journal of tissue engineering”
January 2024 in “Journal of tissue engineering” Sunlight exposure damages hair follicles, but certain stem cell-derived particles can reduce this damage and help with hair regeneration.
 August 2023 in “Military Medical Research”
August 2023 in “Military Medical Research” Scientists have improved 3D models of human skin for research and medical uses, but still face challenges in perfectly replicating real skin.
[object Object]  April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Scientists created skin-like structures from stem cells that include features like hair and sweat glands.
 January 2023 in “Theranostics”
January 2023 in “Theranostics” Mechanical force is important for the first contact between skin cells and hair growth in mini-organs.
 November 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Skin organoids with NCSTN mutation show changes in hair follicle development and higher inflammation, key features of Hidradenitis Suppurativa.
 July 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
July 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Scientists improved how to make skin-like structures from stem cells using special gels and a device that controls growth signals, leading to better hair and skin features.
 92 citations,
August 2017 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America”
92 citations,
August 2017 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” Newborn mouse skin cells can grow hair and this process can be recreated in adult cells to potentially help with hair loss.
 44 citations,
June 2018 in “Journal of Cellular Physiology”
44 citations,
June 2018 in “Journal of Cellular Physiology” Researchers developed a 3D model of human hair follicle cells that can help understand hair growth and test new hair loss treatments.
39 citations,
March 2022 in “Nature Protocols” Scientists created hair-growing skin models from stem cells, which could help treat hair loss and skin diseases.
 31 citations,
May 2019 in “Nature communications”
31 citations,
May 2019 in “Nature communications” Single Blimp1+ cells can create functional sebaceous gland organoids in the lab.
 11 citations,
June 2005 in “Stem Cells and Development”
11 citations,
June 2005 in “Stem Cells and Development” Intestinal stem cells can help repair skin damage from radiation.
 10 citations,
September 2022 in “Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences”
10 citations,
September 2022 in “Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences” SOX9 is essential for the development of various organs and hair follicles.
























