February 1999 in “The anatomical record” Two mouse mutants have defective hair cuticle cross-linking.
309 citations,
October 2007 in “Biomaterials” Keratin from human hair helps nerves heal faster.
163 citations,
October 2001 in “EMBO journal” Overexpressing follistatin in mice delays wound healing and reduces scar size.
99 citations,
May 1998 in “Journal of biological chemistry/The Journal of biological chemistry” Small proline-rich proteins and trichohyalin help make epithelial tissues tougher and more flexible.
81 citations,
December 2007 in “Acta materialia” AFM helped show how hair changes under tension and the effects of damage and conditioner.
68 citations,
February 2011 in “European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics” Keratin films from human hair can potentially replace human nail plates for drug testing.
 39 citations,
June 2019 in “Nanomaterials”
39 citations,
June 2019 in “Nanomaterials” Nanotube-based hair treatments could improve hair health and growth, and offer long-lasting effects.
27 citations,
January 2015 in “International Journal of Trichology” The supplement helps improve hair growth and reduce hair shedding.
20 citations,
October 2021 in “Applied materials today” A new microneedle patch and yellow light therapy significantly promote hair regrowth.
15 citations,
July 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Current hair removal methods improve appearance but need more research for better options.
14 citations,
April 2016 in “PloS one” The KRTAP11-1 gene promoter is crucial for specific expression in sheep wool cortex.
10 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology” Keratin-associated proteins are part of the developing hair fiber cuticle.
9 citations,
January 2011 in “Journal of X-ray science and technology” Perming and bleaching damage hair differently, with bleached hair having more cysteic acid in the cuticle.
8 citations,
January 2023 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Transglutaminase activity is important for skin and is found in both mammals and birds.
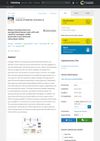 6 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Materials Chemistry B”
6 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Materials Chemistry B” The dressing generates hydrogen sulfide to help heal wounds faster by reducing inflammation and promoting cell growth.
 5 citations,
May 2022 in “Molecules”
5 citations,
May 2022 in “Molecules” Botulinum toxin is effective for various skin conditions, but more research and awareness of side effects are needed.
 5 citations,
January 2020 in “Bioscience Reports”
5 citations,
January 2020 in “Bioscience Reports” Certain changes in the VEGF gene can increase or decrease the risk of polycystic ovary syndrome.
3 citations,
December 2021 in “Materials today communications” A new film made from human hair supports skin cell growth better than collagen.
3 citations,
December 2019 in “Biomaterials Research/Biomaterials research” Calcium and magnesium in hair increase with age and are higher in adult women.
 2 citations,
October 2022 in “Journal of structural biology”
2 citations,
October 2022 in “Journal of structural biology” Older thin hair is not just thinner but also has different shape, structure, and stiffness.
2 citations,
January 2022 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Chemical hair straighteners can cause scalp and hair damage, but long-term effects are unclear.
 1 citations,
August 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology (Print)”
1 citations,
August 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology (Print)” Too much selenium can cause hair loss and nail problems.
October 2024 in “Cosmetics” ATG effectively reduces hair frizz without damaging hair strength.
 May 2024 in “Ultramicroscopy”
May 2024 in “Ultramicroscopy” Atomic Force Microscopy is a more accurate way to assess hair damage and the effect of cosmetic treatments.
The KRT84 gene is linked to better wool quality in Gansu Alpine Fine-wool sheep.
 January 2024 in “Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery”
January 2024 in “Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery” Scalp injuries and harsh hair care can cause severe hair matting in children.
 December 2023 in “Journal of molecular structure”
December 2023 in “Journal of molecular structure” Hair treatments and dehydration affect hair's lipid and protein behavior, influencing its flexibility and appearance.
 November 2023 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics”
November 2023 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics” New hair loss treatment using marine collagen and dissolvable needles improves hair growth.
 November 2023 in “Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers”
November 2023 in “Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers” Scientists made nanoparticles from human hair proteins to improve drug delivery.

Thiolated cyclodextrin-based nanoparticles effectively deliver Minoxidil for scalp treatment without causing skin irritation.











