 15 citations,
June 2019 in “eLife”
15 citations,
June 2019 in “eLife” Activin A and follistatin control when hair cells develop in mouse ears.
 5 citations,
February 2017 in “Biomolecules & Therapeutics”
5 citations,
February 2017 in “Biomolecules & Therapeutics” 4-O-Methylhonokiol helps protect skin cells from growth-stopping effects of a protein by regulating growth-related pathways.
 153 citations,
October 2007 in “Cell Stem Cell”
153 citations,
October 2007 in “Cell Stem Cell” New research suggests that skin cell renewal may not require a special type of cell previously thought to be essential.
[object Object]  July 2019 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
July 2019 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” Activin A speeds up ear hair cell differentiation, while Follistatin slows it down.
137 citations,
January 2006 in “Frontiers in bioscience” CRH in the skin acts like the body's stress response system, affecting cell behavior and immune activity.
22 citations,
April 2012 in “The American journal of pathology” Loss of Msx2 function causes eye development issues similar to Peters anomaly.

Activin A and follistatin control when ear hair cells form in mice.

Activin A promotes ear hair cell development, while follistatin delays it.
 228 citations,
September 2012 in “Trends in Neurosciences”
228 citations,
September 2012 in “Trends in Neurosciences” Nerves are crucial for the regeneration of various body parts in many animals.
 January 2018 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine”
January 2018 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine” The nucleus is key in controlling skin growth and repair by coordinating signals, gene regulators, and epigenetic changes.
 83 citations,
May 2013 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
83 citations,
May 2013 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Skin development in mammals is controlled by key proteins and signals from underlying cells, involving stem cells for maintenance and repair.
48 citations,
March 2010 in “PloS one” C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta are crucial for normal skin and oil gland cell development in adult mice.
253 citations,
April 2008 in “Current opinion in cell biology” Notch signalling helps skin cells differentiate and prevents tumors.
 3 citations,
May 2021 in “Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine”
3 citations,
May 2021 in “Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine” Some traditional Chinese medicines may have anti-aging benefits and could help with hair growth, but more research is needed.
 72 citations,
June 2001 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
72 citations,
June 2001 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” S100A4 and S100A6 proteins may activate stem cells for hair follicle regeneration and could be potential targets for hair loss treatments.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Genetics and Molecular Research”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Genetics and Molecular Research” Stopping S100A3 activity slows down hair growth in mice.
 4 citations,
November 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
4 citations,
November 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Lung and liver macrophages protect our tissues and their dysfunction can cause various diseases.
 38 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology”
38 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology” The document concludes that understanding hair follicle cell cycles is crucial for hair growth and alopecia research, and recommends specific techniques and future research directions.
 27 citations,
January 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology”
27 citations,
January 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology” Immune cells affect hair growth and could lead to new hair loss treatments.
 5 citations,
January 2021 in “iScience”
5 citations,
January 2021 in “iScience” Using a combination of specific cell cycle regulators is better for safely keeping hair root cells alive indefinitely compared to cancer-related methods.
 52 citations,
May 2015 in “PLOS Genetics”
52 citations,
May 2015 in “PLOS Genetics” miR-22, a type of microRNA, controls hair growth and its overproduction can cause hair loss, while its absence can speed up hair growth.
45 citations,
April 2001 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Different Myc family proteins are located in various parts of the hair follicle and may affect stem cell behavior.
 31 citations,
April 2016 in “Nature communications”
31 citations,
April 2016 in “Nature communications” Certain signals are important for reducing specific chemical markers on hair follicle stem cells during rest periods, which is necessary for healthy hair growth.
 153 citations,
January 2001 in “Science”
153 citations,
January 2001 in “Science” Using CDK inhibitors on rats showed a reduction in chemotherapy-caused hair loss, but later experiments could not repeat these results.
 20 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
20 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Graying hair happens due to aging and might be delayed by new treatments.
August 2024 in “Food Bioscience” Bifidobacterium longum BB536 metabolites may help treat hair loss by repairing and promoting hair cell growth.
[object Object]  66 citations,
March 2019 in “Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences”
66 citations,
March 2019 in “Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences” Melanocyte development from neural crest cells is complex and influenced by many factors, and better understanding could help treat skin disorders.
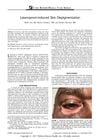 9 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Glaucoma”
9 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Glaucoma” Latanoprost eye drops may cause skin depigmentation.
 February 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
February 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Hair loss in Androgenetic Alopecia is caused by genetics, aging, and lifestyle, leading to hair follicle shrinkage and related health risks.
 60 citations,
June 1997 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
60 citations,
June 1997 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Apoptosis is crucial for healthy skin and treating skin diseases.
























