Combinatorial Expression of Cell Cycle Regulators Is More Suitable for Immortalization Than Oncogenic Methods in Dermal Papilla Cells
January 2021
in “
iScience
”
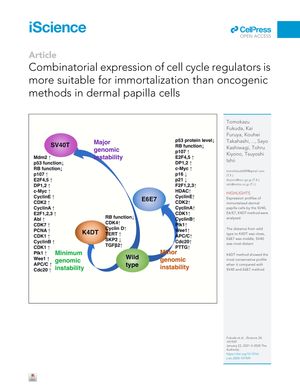
TLDR Using a combination of specific cell cycle regulators is better for safely keeping hair root cells alive indefinitely compared to cancer-related methods.
The document presents a study that compared three methods of immortalizing human dermal papilla cells (DPCs): SV40, E6/E7, and K4DT. The K4DT method, which involves the combinatorial expression of mutant CDK4, cyclin D1, and TERT, was found to be the most suitable for maintaining the original characteristics of DPCs with minimal genomic instability. RNA sequencing analysis showed that K4DT immortalized cells had a gene expression profile closest to wild-type cells, and chromosome analysis revealed that 95% of K4DT cells had a normal human chromosome count of 46. In contrast, SV40 and E6/E7 methods resulted in significant chromosomal abnormalities. The study concluded that the K4DT method is preferable for in vitro cellular modeling of human and animal diseases due to its ability to cause the fewest genomic abnormalities in DPCs. The study acknowledges limitations and suggests further evaluations with larger biological replicates.





