 12 citations
,
June 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy”
12 citations
,
June 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy” Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) can promote new hair growth and increase hair density, but its effectiveness varies depending on the type of hair loss.
 12 citations
,
June 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
12 citations
,
June 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Platelet-rich plasma is tolerable for lichen planopilaris and doesn't worsen the condition, but its effectiveness is unclear.
 11 citations
,
April 2020 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
11 citations
,
April 2020 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Taking oral isotretinoin with creams worked better for treating a type of hair loss than creams alone.
 11 citations
,
February 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy”
11 citations
,
February 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy” Low-Level Light Therapy significantly reduced inflammation and promoted hair regrowth in patients with Lichen planopilaris.
 16 citations
,
February 2020 in “The Laryngoscope”
16 citations
,
February 2020 in “The Laryngoscope” Hair transplants can work for frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planopilaris, but results are less favorable and the conditions can develop after the transplant.
 24 citations
,
January 2020 in “JAAD Case Reports”
24 citations
,
January 2020 in “JAAD Case Reports” Topical metformin helped regrow hair in two women with a hard-to-treat scarring hair loss condition.
 15 citations
,
August 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
15 citations
,
August 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) may help treat hair loss in patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia who don't respond to other treatments.
 16 citations
,
June 2019 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
16 citations
,
June 2019 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Type 2 diabetes may increase the risk of severe hair loss in African American women.
 95 citations
,
February 2019 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
95 citations
,
February 2019 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Mutations in the PADI3 gene are linked to a higher risk of scarring hair loss in women of African descent.
 8 citations
,
October 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations
,
October 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The review suggests there's no agreed treatment for Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, but hydroxychloroquine and 5a-reductase inhibitors are most effective. New treatments like platelet-rich plasma and LED light could help if standard treatments fail.
 27 citations
,
September 2018 in “Skin appendage disorders”
27 citations
,
September 2018 in “Skin appendage disorders” Hair transplantation may work for some types of scarring alopecia, but results vary and more research is needed.
 28 citations
,
August 2018 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
28 citations
,
August 2018 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) may help improve hair density in primary cicatricial alopecias (PCAs) patients, but more trials are needed to confirm its benefits.
11 citations
,
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” The book helps surgeons improve hair transplants for Asian patients.
 80 citations
,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
80 citations
,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Low-dose oral minoxidil and spironolactone combo effectively reduces hair loss and improves hair density in women.
 16 citations
,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
16 citations
,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Low-level laser therapy may reduce symptoms and increase hair thickness in lichen planopilaris patients.
 27 citations
,
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
27 citations
,
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Hair loss in black women needs more research, early intervention, and community education.
 52 citations
,
May 2017 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
52 citations
,
May 2017 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” PRP injections improve hair density and thickness in women with hair loss.
 178 citations
,
April 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
178 citations
,
April 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil, finasteride, and low-level laser light therapy effectively treat hair loss.
 95 citations
,
November 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
95 citations
,
November 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Treatments for permanent hair loss from scarring aim to stop further loss, not regrow hair, and vary by condition, with partial success common.
 39 citations
,
January 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
39 citations
,
January 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” Injecting platelet-rich plasma during hair transplant surgery improves hair regrowth rate, speeds up skin recovery, and enhances hair quality.
 12 citations
,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders”
12 citations
,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” Hair restoration surgery can potentially treat primary scarring alopecias, but it's important to start early medication, ensure patient remission before transplant, and monitor after surgery.
 24 citations
,
September 2015 in “JAAD case reports”
24 citations
,
September 2015 in “JAAD case reports” Finasteride helps hair regrowth in frontal fibrosing alopecia.
 144 citations
,
July 2015 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
144 citations
,
July 2015 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disease affecting about 2% of people, causing significant disability and often associated with mental health issues and other autoimmune conditions.
 66 citations
,
June 2015 in “Aesthetic Plastic Surgery”
66 citations
,
June 2015 in “Aesthetic Plastic Surgery” Platelet preparations generally show positive effects on wound healing and facial rejuvenation, but more thorough research is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
 28 citations
,
January 2015 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
28 citations
,
January 2015 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Women with scarring alopecia have a lower quality of life and more anxiety and depression than those with non-scarring alopecia.
 25 citations
,
September 2014 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
25 citations
,
September 2014 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Hair transplants can effectively treat hair loss from CCCA in African American women if there's no inflammation.
 47 citations
,
June 2014 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
47 citations
,
June 2014 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Most treatments for lichen planopilaris were found to be generally unsatisfactory.
 8 citations
,
March 2014 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
8 citations
,
March 2014 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Specialized techniques are needed for hair restoration in individuals with curly Afrocentric hair due to unique challenges.
 339 citations
,
February 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
339 citations
,
February 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Most patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia are postmenopausal women, and treatments like finasteride and dutasteride can improve or stabilize the condition.
 165 citations
,
August 2013 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
165 citations
,
August 2013 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Low-Level Laser Therapy is effective and safe for hair growth with minimal side effects.
 41 citations
,
August 2013 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
41 citations
,
August 2013 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” FUE provides minimal scarring and quick recovery in hair transplantation, and surgeons not using it may lag in technology.
220 citations
,
June 2013 in “The Journal of Pathology” Lichen planopilaris may be an autoimmune disease causing hair loss due to immune system issues in hair follicles.
 48 citations
,
May 2013 in “Canadian Medical Association Journal”
48 citations
,
May 2013 in “Canadian Medical Association Journal” Primary cicatricial alopecia, a rare disorder causing permanent hair loss, is hard to diagnose and treat, with treatments like anti-inflammatory drugs and steroids offering varied results and no guaranteed cure. Psychological support for patients is important, and future research should aim to identify causes of the condition.
45 citations
,
April 2013 in “Dermatologic surgery” Hair transplantation might work for some people with frontal fibrosing alopecia, but more research is needed.
 44 citations
,
September 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology”
44 citations
,
September 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology” Hair breakage may be an early sign of a hair loss condition called CCCA in African American women.
 270 citations
,
March 2012 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
270 citations
,
March 2012 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Platelet-rich plasma can potentially promote hair growth by stimulating cell growth and increasing certain proteins.
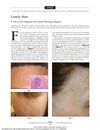 63 citations
,
October 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
63 citations
,
October 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Isolated long hairs at the original hairline can help diagnose Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia.
 150 citations
,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology”
150 citations
,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology” The document concludes that more research is needed to better understand and treat primary cicatricial alopecias, and suggests a possible reclassification based on molecular pathways.
159 citations
,
August 2010 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Hydroxychloroquine effectively reduces symptoms of frontal fibrosing alopecia, especially in the first 6 months.
 53 citations
,
May 2010 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
53 citations
,
May 2010 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Hair transplantation may not work for Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia as transplanted hair was lost when the disease came back.
 54 citations
,
August 2009 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
54 citations
,
August 2009 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Modern hair transplants use small grafts for a natural look and drugs to prevent further loss, with high patient satisfaction.
 14 citations
,
July 2009 in “Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery”
14 citations
,
July 2009 in “Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery” Hair restoration techniques like follicular unit transplant surgery and follicular unit extraction are effective, with ideal graft placement density between 20-30 units per cm². Medications like Minoxidil and Finasteride can help maintain and regrow hair.
 160 citations
,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
160 citations
,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” New insights show Lichen Planopilaris is a rare, scarring hair loss condition, hard to treat, mainly affecting middle-aged women, and significantly impacts mental health.
69 citations
,
January 2009 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal” Successful hair transplants need good communication, careful planning, skilled surgery, and proper aftercare.
 98 citations
,
May 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
98 citations
,
May 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” There are many treatments for permanent hair loss disorders, but their effectiveness varies and there's no clear best option.
 126 citations
,
April 2006 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
126 citations
,
April 2006 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The conclusion is that FFA and LPP have similar scalp biopsy features, making them hard to distinguish histologically, and FFA may be a specific kind of scarring hair loss.
46 citations
,
March 2006 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Current treatments for cicatricial alopecia can manage symptoms but don't stop hair loss or the disease.
 203 citations
,
December 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
203 citations
,
December 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Early diagnosis and treatment, using finasteride, minoxidil, or hair transplantation, improves hair loss outcomes.
254 citations
,
December 2003 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Accurate diagnosis and aggressive treatment are crucial to prevent permanent hair loss in cicatricial alopecia.
 153 citations
,
August 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
153 citations
,
August 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a less invasive hair transplant method with minimal scarring, suitable for about 60% of patients, especially those needing fewer grafts and quicker recovery.
107 citations
,
September 1968 in “Archives of Dermatology” Using hot combs can cause permanent hair loss on the scalp's crown.



















































