 3 citations,
December 2022 in “Cells”
3 citations,
December 2022 in “Cells” Cannabinoids like CBD and THC may help treat non-cancer skin diseases, but more research is needed.
1 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology” Genetic screening for NUDT15 polymorphisms is crucial for patients taking azathioprine, especially in Asians.
 November 2024 in “Rheumatology Advances in Practice”
November 2024 in “Rheumatology Advances in Practice” Early recognition and treatment of SLE can improve outcomes in patients with complex symptoms.
488 citations,
July 2021 in “Cell” Fibroblasts are crucial for tissue repair and inflammation, and understanding them can help treat fibrotic diseases.
227 citations,
November 2004 in “Medicine” Older adults diagnosed with lupus show less severe symptoms but have a lower survival rate, often due to age-related factors.
63 citations,
September 2020 in “Frontiers in Microbiology” Probiotics show promise for health benefits but need more research to understand how they work.
 54 citations,
January 2023 in “Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy”
54 citations,
January 2023 in “Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy” New therapies are being developed that target integrin pathways to treat various diseases.
47 citations,
August 2016 in “American Journal Of Pathology” Fibroblast changes in systemic sclerosis may help understand disease severity and treatment.
44 citations,
October 2020 in “Arthritis Care & Research” Choosing the right tools is crucial for accurately measuring lupus activity and damage.
44 citations,
August 2014 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Methotrexate is a promising and safe treatment for severe alopecia areata, with better results when combined with corticosteroids.
22 citations,
January 2012 in “Mediators of inflammation” Nonantibiotic macrolides show promise for treating various inflammatory skin conditions.
 12 citations,
August 2022 in “Biochemical Journal”
12 citations,
August 2022 in “Biochemical Journal” Different types of cell death affect skin health and inflammation, and understanding them could improve treatments for skin diseases.
 10 citations,
November 2021 in “Biomedicines”
10 citations,
November 2021 in “Biomedicines” Some therapies using stem cells and platelet-rich plasma may help treat osteoarthritis, but more research is needed to ensure they are safe and effective.
9 citations,
June 2023 in “Cells” Certain natural and synthetic compounds may help treat inflammatory skin diseases by targeting a specific signaling pathway.
 7 citations,
July 2019 in “International archives of internal medicine”
7 citations,
July 2019 in “International archives of internal medicine” Common skin conditions can greatly affect a person's mental health and social life.
 3 citations,
June 2023 in “MedComm”
3 citations,
June 2023 in “MedComm” Stem cells and their exosomes show promise for repairing tissues and healing wounds when delivered effectively, but more research is needed on their tracking and optimal use.

Celiac disease requires more than just a gluten-free diet for effective management.
 January 2025 in “AAPS PharmSciTech”
January 2025 in “AAPS PharmSciTech” Transethosomes improve drug delivery through the skin and show promise for treating various conditions.
 January 2024 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
January 2024 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Non-biologic immunosuppressive drugs are crucial for treating autoimmune and chronic inflammatory skin diseases.
 August 2023 in “Tzu Chi Medical Journal”
August 2023 in “Tzu Chi Medical Journal” Iron deficiency is the main cause of hair loss in women, and iron supplements started within 6 months can improve hair health.

A man wrongly believed he had parasites, showing that delusional infestation can affect men and is often linked with other psychiatric issues, but can be treated with antipsychotics.
 6 citations,
November 2023 in “Clinical Pharmacokinetics”
6 citations,
November 2023 in “Clinical Pharmacokinetics” Ritlecitinib shows promise as a versatile treatment for various autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
 11 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
11 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Oral tofacitinib helped regrow hair in over half of the patients with severe alopecia, but relapses and side effects were common.
 24 citations,
January 2014 in “The American Journal of Chinese Medicine”
24 citations,
January 2014 in “The American Journal of Chinese Medicine” The leaves of Platycladus orientalis have potential health benefits but require more research for safety and understanding how they work.
 2 citations,
April 2023 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
2 citations,
April 2023 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” JAK-inhibitors for alopecia areata are generally safe with mostly mild side effects and a low rate of treatment withdrawal.

Psoriasis is linked to a higher risk of autoimmune diseases and other health conditions.

People with psoriasis have more health problems, including autoimmune diseases, than those without it.
 June 2023 in “Fundamental & clinical pharmacology”
June 2023 in “Fundamental & clinical pharmacology” JAK inhibitors help treat some diseases but may increase risks of blood clots and cancer in certain patients.
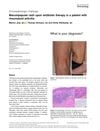 1 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Methotrexate caused a rare skin rash in a rheumatoid arthritis patient, which resolved after stopping the drug.
 February 2013 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
February 2013 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Oral propranolol successfully treated a baby's skin growth and ulceration linked to PELVIS syndrome.





















