Maculopapular Rash Upon Antibiotic Therapy in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis
November 2020
in “
International Journal of Dermatology
”
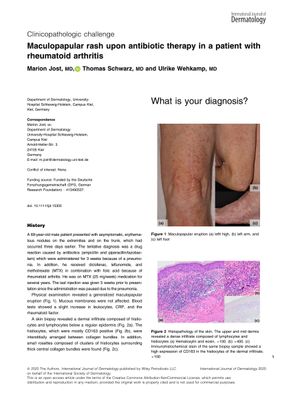
TLDR Methotrexate caused a rare skin rash in a rheumatoid arthritis patient, which resolved after stopping the drug.
A 69-year-old male with rheumatoid arthritis developed asymptomatic, erythematous nodules after receiving antibiotics for pneumonia. The nodules were initially suspected to be a drug reaction but were later identified as methotrexate (MTX)-induced rheumatoid papular eruption, a rare side effect of MTX in rheumatic patients. Histopathological examination revealed characteristic granulomatous rosettes without epidermal involvement. The rash resolved completely after MTX withdrawal, confirming the diagnosis. This case highlighted the uncommon delayed onset of the eruption and suggested a possible trigger from the extended bronchopulmonary infection. MTX-induced skin reactions are rare and predominantly occur in rheumatic conditions.





