 1 citations,
February 2004
1 citations,
February 2004 Skin diseases are common and can significantly affect people's lives; better outcome measures and ethical clinical trials are needed to improve dermatology care.
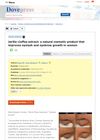 1 citations,
January 2019 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
1 citations,
January 2019 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Jarilla-Coffea extract gel effectively and safely increases eyelash and eyebrow thickness in women.
[object Object]  8 citations,
February 2005 in “Veterinary dermatology”
8 citations,
February 2005 in “Veterinary dermatology” Chesapeake Bay retrievers' hair loss is likely a breed-specific, hereditary condition linked to abnormal steroid levels and distinct skin changes.
 25 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery”
25 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery” PRP injections help regrow hair, reduce hair loss, and increase hair thickness, but effects decrease without ongoing treatment.
 March 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
March 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” Severe alopecia areata greatly impacts quality of life, mental health, and daily activities.
 January 2025 in “SKIN The Journal of Cutaneous Medicine”
January 2025 in “SKIN The Journal of Cutaneous Medicine” Baricitinib treatment for severe alopecia areata shows significant improvement by 52 weeks, especially in very severe cases.
[object Object]  18 citations,
June 2010 in “Journal of Chromatography B”
18 citations,
June 2010 in “Journal of Chromatography B” New method measures finasteride in blood quickly and accurately.
 April 2015 in “Andrology”
April 2015 in “Andrology” HNG may help prevent the negative effects of chemotherapy on sperm production and white blood cell counts.
 7 citations,
December 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
7 citations,
December 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” COVID-19 can cause hair loss starting as early as 18 days after infection.
 May 2024 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
May 2024 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Heat-treated Limosilactobacillus fermentum with menthol, salicylic acid, and panthenol promotes hair growth and balances scalp microbiome in people with androgenetic alopecia.
1 citations,
May 2021 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Iontophoresis with growth factors safely and effectively promotes hair regrowth without discomfort.
 26 citations,
July 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
26 citations,
July 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” The review suggests that a special cell-derived treatment shows promise for various skin conditions and hair growth but needs more research for confirmation.
 1 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of stem cell research and medicine”
1 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of stem cell research and medicine” Fat-derived stem cell therapies can potentially increase hair growth and thickness in people with hair loss.
 81 citations,
August 2014 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
81 citations,
August 2014 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Red light therapy is safe and effectively increases hair growth in women with hair loss.
 7 citations,
January 2009 in “Immunological investigations”
7 citations,
January 2009 in “Immunological investigations” A 3-year-old boy lost all his hair due to a rare reaction to phenobarbital, but it grew back after steroid treatment.
 66 citations,
November 2001 in “European journal of endocrinology”
66 citations,
November 2001 in “European journal of endocrinology” Low SHBG and high FAI, FT, and DHEAS levels are effective in identifying PCOS.
 11 citations,
January 2014 in “The Scientific World Journal”
11 citations,
January 2014 in “The Scientific World Journal” Cynatine HNS improves hair and nail quality in 90 days.
March 2024 in “Journal of functional biomaterials” A kimchi-derived bacterium could help whiten teeth and prevent bad breath.
 11 citations,
April 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
11 citations,
April 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Certain genetic variations in OCT1 may improve insulin sensitivity with metformin in women with PCOS.
 21 citations,
January 2012 in “Annals of Dermatology”
21 citations,
January 2012 in “Annals of Dermatology” 17α-Estradiol solution safely improves hair density and thickness in female pattern hair loss.
 April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The booklet increased melanoma patients' knowledge about lymphedema by 13%.
 1 citations,
December 2022 in “BMC Public Health”
1 citations,
December 2022 in “BMC Public Health” Long-term effects of COVID-19 can vary over time and are more likely in certain age and gender groups, while race, income, and education levels have little to no impact. Ongoing medical care is needed due to potential complications.
 19 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
19 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Acne lesions start with changes in hair follicles and increase in inflammation, suggesting a cycle that could affect treatment strategies.
 September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Thermal imaging is a useful non-invasive method to diagnose active inflammation in frontal fibrosing alopecia.
15 citations,
December 2021 in “Pharmaceutics” The study found key factors in the cause of hidradenitis suppurativa, its link to other diseases, and identified existing drugs that could potentially treat it.
1 citations,
November 2023 in “Life” Hyaluronic acid injections can improve mouth opening and quality of life in scleroderma patients.
 2 citations,
October 2022 in “International journal of Ayurvedic medicine”
2 citations,
October 2022 in “International journal of Ayurvedic medicine” Licorice has many traditional health benefits, but more research is needed to fully support these claims.
 19 citations,
May 2020 in “Cells”
19 citations,
May 2020 in “Cells” Substance from human umbilical cord blood cells promotes hair growth.
 November 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
November 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Genes controlling hair growth and immune response are disrupted in male pattern baldness.
IVL-DrugFluidic® can mass-produce high-quality, long-acting injectable drug microspheres, improving patient compliance and reducing side effects.

























