98 citations,
July 1968 in “Archives of Dermatology” Human sebum can cause acne by clogging pores.
 63 citations,
February 2013 in “Human cell”
63 citations,
February 2013 in “Human cell” PEGL-DOX causes Hand-Foot Syndrome due to skin reactions from prolonged circulation and ROS generation.
63 citations,
May 2009 in “Dermato-endocrinology” Increased FGFR2b signaling, influenced by androgens, plays a role in causing acne.
 60 citations,
January 1989 in “Toxicologic Pathology”
60 citations,
January 1989 in “Toxicologic Pathology” Using minoxidil on dogs can cause serious cardiovascular damage, including arterial injury and hemorrhagic lesions.
 52 citations,
April 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
52 citations,
April 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Male pattern baldness involves three mechanisms and finasteride can help reverse it.
35 citations,
March 1976 in “British Journal of Dermatology” No clear link was found between hair follicle mites and skin conditions in Australian Aborigines.
 34 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
34 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Scalp cooling is the most effective FDA-approved method to prevent chemotherapy-induced hair loss, but more research is needed for other treatments.
24 citations,
May 2017 in “Annals of botany” Pathogenic Pseudomonas syringae bacteria stimulate early root hair growth in Arabidopsis plants.
19 citations,
August 2018 in “JAMA dermatology” Mesenchymal stem cells in people with Hidradenitis Suppurativa are more inflammatory, possibly contributing to the disease.
 1 citations,
January 2006
1 citations,
January 2006 Hirsutism is mainly caused by high androgen levels or sensitivity, with PCOS being the most common cause.
 January 2025 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
January 2025 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Hair follicles are key to treating vitiligo and alopecia areata, but challenges exist.
 December 2024 in “Frontiers in Genetics”
December 2024 in “Frontiers in Genetics” EGFR and mTOR inhibitors may help manage Olmsted syndrome symptoms.
April 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Alopecia areata and vitiligo share immune system dysfunction but differ in specific immune responses and affected areas.
 June 2023 in “Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)”
June 2023 in “Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)” Inflammation in hair follicles is a key risk factor for developing common baldness.
 January 2023 in “Sibirskij medicinskij vestnik”
January 2023 in “Sibirskij medicinskij vestnik” Women with PCOS are more vulnerable to severe COVID-19 and related health issues.

Androgenetic alopecia, or hair loss, is caused by a mix of genetics, hormones, and environment, where testosterone affects hair growth and causes hair to become smaller and grow for a shorter time.
 April 2022 in “Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan Media Husada”
April 2022 in “Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan Media Husada” Telogen effluvium is a common, reversible hair loss condition treatable with patient education and sometimes Minoxidil.
 November 2020 in “Journal of Bioengineering and Technology Apllied for Health”
November 2020 in “Journal of Bioengineering and Technology Apllied for Health” COVID-19 affects multiple body systems and complicates treatment; accurate testing is crucial.
 June 2019 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
June 2019 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Alopecia in patients with epidermolysis bullosa varies in severity and is often caused by skin blistering or trauma.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that targets hair follicles.
January 2006 in “Practical Journal of Clinical Medicine”  March 2019 in “Chinese Journal of Dermatology”
March 2019 in “Chinese Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss, known as androgenetic alopecia, is mainly caused by genetics, but also by hormone imbalances, shrinking hair follicles, inflammation, and environmental factors.
 150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology”
150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology” The document concludes that more research is needed to better understand and treat primary cicatricial alopecias, and suggests a possible reclassification based on molecular pathways.
 135 citations,
April 2017 in “Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine”
135 citations,
April 2017 in “Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine” New treatments for PCOS show promise, including both medication and non-medication options.
 89 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
89 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Alopecia areata is likely caused by a combination of genetic factors and immune system dysfunction, and may represent different diseases with various causes.
 28 citations,
January 2000 in “Medical Mycology”
28 citations,
January 2000 in “Medical Mycology” Fungal infections in lab animals can interfere with research.
 23 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
23 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disease affecting hair follicles, influenced by genetic and environmental factors, with rodent models being essential for research.
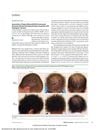 5 citations,
July 2020 in “JAMA Dermatology”
5 citations,
July 2020 in “JAMA Dermatology” Minoxidil solution applied twice daily improved hair growth in patients with Woolly Hair/Hypotrichosis due to LIPH gene issues, with mild side effects.
 3 citations,
January 2010 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
3 citations,
January 2010 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Immunization and throat bacteria may increase the risk of a hair loss condition called alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
January 1989 in “Journal of dermatological treatment”
1 citations,
January 1989 in “Journal of dermatological treatment” Azelaic acid may help treat acne by killing bacteria, reducing inflammation, and preventing clogged pores.





















