 3 citations,
April 2010 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
3 citations,
April 2010 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Most people with scarring and nonscarring hair loss show similar D2-40 levels, but some with scarring hair loss have higher levels.
178 citations,
June 1994 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Alopecia areata in these mice is inherited, more common in young females, and can be treated with triamcinolone acetonide.
 3 citations,
January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders”
3 citations,
January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders” Some people with a history of autoimmune hair loss experienced worsening symptoms after COVID-19 vaccination.
 23 citations,
July 1982 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
23 citations,
July 1982 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The review concludes that accurate diagnosis of different types of hair loss requires proper biopsy techniques and understanding the hair growth cycle and underlying causes.
November 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks” Female androgenic alopecia causes hair thinning in women, especially after menopause, and affects their mental well-being.
4 citations,
May 2018 in “European journal of dermatology/EJD. European journal of dermatology” Fumaric acid esters might help treat alopecia areata, but more research is needed.
 1 citations,
July 2014 in “Our Dermatology Online”
1 citations,
July 2014 in “Our Dermatology Online” The patient with both scarring and non-scarring hair loss showed complex immune reactions and improved with steroid treatment.
 July 2019 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences”
July 2019 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences” Oral cyclosporine works better than betamethasone minipulse therapy for treating Alopecia Areata.
1 citations,
April 2024 in “Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology” Microneedles combined with conventional therapies show promise in treating alopecia areata.
 33 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Crohn's and colitis”
33 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Crohn's and colitis” Alopecia Areata might be linked to Crohn's disease.
 August 2021 in “Revista Colombiana de Reumatología/Revista Colombiana de Reumatologia”
August 2021 in “Revista Colombiana de Reumatología/Revista Colombiana de Reumatologia” Janus kinase inhibitors may effectively treat severe alopecia areata unresponsive to other treatments.
19 citations,
August 2019 in “Dermatologic therapy” Janus kinase inhibitors show promise for treating alopecia areata but need more research for confirmation.
 11 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
11 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Stopping JAK inhibitor treatment for hair loss can lead to worse hair loss than before the treatment.
 July 2018 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
July 2018 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” Higher levels of miR-203 may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata.
 July 2024 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
July 2024 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Certain immune cells are linked to non-scarring hair loss, suggesting potential for immune-targeted treatments.
 2 citations,
January 2019 in “Case Reports in Dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2019 in “Case Reports in Dermatology” A 66-year-old woman's thick scalp and hair loss were confirmed as lipedematous alopecia, a rare condition possibly influenced by genetics, with no effective treatment known.
 4 citations,
February 2022 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
4 citations,
February 2022 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Monocytes might be linked to hair loss after COVID-19.
 11 citations,
January 2022 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
11 citations,
January 2022 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Alopecia areata is a chronic condition causing hair loss, with new treatments targeting the immune system showing promise.
32 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Temporal triangular alopecia is a non-scarring hair loss in children, often linked to other health conditions.
 December 2016 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
December 2016 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” Skin problems are common in thyroid disorders, with dry skin in hypothyroidism and warm, soft skin in hyperthyroidism.
 February 2024 in “The Open dermatology journal”
February 2024 in “The Open dermatology journal” Alopecia Areata affects people of all ages worldwide, is likely caused by genetic and environmental factors, and can lead to stress and depression, highlighting the need for treatments that address both physical and mental health.
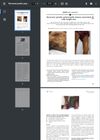 October 2022 in “JAAD case reports”
October 2022 in “JAAD case reports” A man with itchy skin lesions and weight loss was diagnosed with a rare skin condition linked to a pancreatic tumor.
 March 2019 in “Chinese Journal of Dermatology”
March 2019 in “Chinese Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss, known as androgenetic alopecia, is mainly caused by genetics, but also by hormone imbalances, shrinking hair follicles, inflammation, and environmental factors.
 2 citations,
November 2018 in “Destaques Acadêmicos”
2 citations,
November 2018 in “Destaques Acadêmicos” Microneedling showed the most significant results for treating hair thinning in Androgenetic Alopecia.

COVID-19 infection is highly related to increased hair loss, especially in women.

Hair loss after COVID-19 is common, starts sooner in severe cases, and often comes with scalp pain.
 August 2024 in “International Journal of Health Science”
August 2024 in “International Journal of Health Science” Telogen Effluvium (TE) significantly affects women due to stress and hormonal changes, requiring better public health policies and mental health support.
 23 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
23 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The document concludes that we need more research to understand Telogen Effluvium and find effective treatments.

Hair microscopy is a useful and affordable way to diagnose hair disorders.
 33 citations,
April 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
33 citations,
April 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Damaged hair follicle stem cells can cause permanent hair loss, but understanding their role could lead to new treatments.
























