1 citations,
September 2021 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” Minoxidil can help transgender males grow facial hair before starting testosterone therapy.
 May 2023 in “International journal of pharmaceutical sciences and medicine”
May 2023 in “International journal of pharmaceutical sciences and medicine” Sunflower oil was found to promote hair growth in mice with hormone-induced hair loss.
[object Object]  1 citations,
July 2019 in “Medicina Clínica (English Edition)”
1 citations,
July 2019 in “Medicina Clínica (English Edition)” Tofacitinib partially improved hair regrowth in a patient with severe hair loss.
 78 citations,
April 1984 in “Archives of Dermatology”
78 citations,
April 1984 in “Archives of Dermatology” Minoxidil can help regrow hair in alopecia areata patients.
 28 citations,
September 2019 in “International Journal of Nanomedicine”
28 citations,
September 2019 in “International Journal of Nanomedicine” Minoxidil nanoparticles can potentially be a more effective treatment for hair growth than current treatments.
 22 citations,
October 2019 in “Cerebral cortex”
22 citations,
October 2019 in “Cerebral cortex” Sex neurosteroids cause different effects on hippocampal synaptic plasticity in males and females.
 14 citations,
September 1991 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
14 citations,
September 1991 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Minoxidil slows down keratinocyte growth without being toxic.
 19 citations,
July 1983 in “American Journal of Kidney Diseases”
19 citations,
July 1983 in “American Journal of Kidney Diseases” Minoxidil lowers blood pressure in kids with kidney issues, but use carefully due to side effects.
 5 citations,
February 1996 in “Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics/Clinical pharmacology & therapeutics”
5 citations,
February 1996 in “Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics/Clinical pharmacology & therapeutics” Minoxidil given intravenously caused small changes in diastolic blood pressure and increased heart rate at higher concentrations in patients with high blood pressure.
 1 citations,
August 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” The "After Minoxidil" spray makes hair easier to style, less greasy, and encourages people to keep using the treatment.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Many treatments for hair loss show potential, but more testing is needed to confirm their effectiveness. Only minoxidil for women and minoxidil and finasteride for men are FDA approved.
 80 citations,
October 1983 in “BMJ”
80 citations,
October 1983 in “BMJ” Minoxidil helps hair regrowth in alopecia patients, with 16 having good results and no side effects.
 57 citations,
July 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
57 citations,
July 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Stopping minoxidil treatment resumes balding; continuous use needed for results.
 40 citations,
September 2017 in “F1000Research”
40 citations,
September 2017 in “F1000Research” Oral minoxidil effectively reduces hair shedding in women with CTE, with no major side effects.
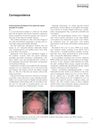 12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A woman developed a scalp condition from using minoxidil, which improved with a different treatment but left scarring.
 10 citations,
December 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
10 citations,
December 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Minoxidil and spironolactone combo effectively treats androgenetic alopecia, improving hair density and diameter.
 2 citations,
December 2019 in “Biomedical dermatology”
2 citations,
December 2019 in “Biomedical dermatology” Minoxidil works faster, but ketoconazole is a safer alternative for female hair loss.
 149 citations,
June 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
149 citations,
June 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil works better for female hair loss, but cyproterone reduces scalp oiliness and causes menstrual issues.
 39 citations,
March 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
39 citations,
March 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Topical minoxidil is a safe and effective treatment for hair loss caused by androgenetic alopecia.
[object Object]  14 citations,
August 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
14 citations,
August 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Low-dose oral minoxidil is a safe treatment for hair loss, with the main side effect being excessive hair growth. Other side effects like foot swelling, low blood pressure when standing, and heart rate changes are rare.
 12 citations,
August 2017 in “Archives of Pharmacal Research”
12 citations,
August 2017 in “Archives of Pharmacal Research” Lecithin-based microparticles can deliver minoxidil for hair growth effectively with less skin irritation.
 9 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology”
9 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology” Scientists developed a new method to deliver alopecia treatment directly to hair follicles, which could be a promising treatment for hair loss and other hair diseases.
 5 citations,
January 2018 in “Javma-journal of The American Veterinary Medical Association”
5 citations,
January 2018 in “Javma-journal of The American Veterinary Medical Association” A dog fully recovered from minoxidil poisoning after receiving treatment.
 3 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
3 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Using 3% topical minoxidil can help women with hair loss, but more research is needed.
 July 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
July 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” A woman experienced excessive hair growth after using a hair loss treatment with minoxidil.
 17 citations,
August 1967 in “JAMA”
17 citations,
August 1967 in “JAMA” The rapid corticotropin test is a quick and simple way to diagnose adrenal insufficiency.
 8 citations,
March 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
8 citations,
March 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Researchers created immortal human skin cells with constant testosterone receptor activity to study hair loss and test treatments.
 53 citations,
January 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
53 citations,
January 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” UVB radiation harms hair growth and health, causing cell death and other changes in human hair follicles.
 7 citations,
June 2021 in “Cell Proliferation”
7 citations,
June 2021 in “Cell Proliferation” Low oxygen levels improve the function of hair and skin cells when they are in direct contact.
 25 citations,
July 2019 in “Journal of drug delivery science and technology”
25 citations,
July 2019 in “Journal of drug delivery science and technology” Researchers created better skin-application menthol capsules that are stable, safe, and penetrate the skin quickly.




























