7 citations,
January 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” NIPP1 is important for healthy skin and could help treat skin inflammation.
 1 citations,
March 2023 in “Aggregate”
1 citations,
March 2023 in “Aggregate” A new hydrogel with micronized amnion helps achieve better, scar-free skin healing.
 48 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms”
48 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms” Hair follicles offer promising targets for delivering drugs to treat hair and skin conditions.
 16 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology”
16 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology” Minoxidil may help treat hair loss by reducing inflammation-related gene activity in skin cells.
 1160 citations,
November 2018 in “Physiological Reviews”
1160 citations,
November 2018 in “Physiological Reviews” The document concludes that better targeted treatments are needed for wound healing, and single-cell technologies may improve cell-based therapies.
 27 citations,
January 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology”
27 citations,
January 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology” Immune cells affect hair growth and could lead to new hair loss treatments.
 160 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine”
160 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine” Telocytes might help with skin repair and regeneration.
353 citations,
July 2015 in “Molecular immunology” Porcine skin is very similar to human skin, making it a useful model for research.
55 citations,
October 2019 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” The review suggests that other immune cells besides CD8+ T cells may contribute to alopecia areata and that targeting regulatory cell defects could improve treatment.
 290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, influenced by genetics, stress, and diet, and may be prevented by a high soy oil diet.
 60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology”
60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology” Lymphocytes, especially CD8+ T cells, play a key role in causing alopecia areata, and targeting them may lead to new treatments.
 1 citations,
June 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
June 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Fetal skin has unique immune cells different from adult skin.
 69 citations,
June 2017 in “Experimental Biology and Medicine”
69 citations,
June 2017 in “Experimental Biology and Medicine” Advanced human skin models improve drug development and could replace animal testing.
April 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Alopecia areata and vitiligo share immune system dysfunction but differ in specific immune responses and affected areas.
253 citations,
December 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair follicles prevent NK cell attacks to avoid hair loss.
 5 citations,
January 2019 in “Elsevier eBooks”
5 citations,
January 2019 in “Elsevier eBooks” Current therapies cannot fully regenerate adult skin without scars; more research is needed for scar-free healing.
 12 citations,
January 2009 in “Stembook”
12 citations,
January 2009 in “Stembook” Improved understanding of stem cell mechanisms can enhance skin tissue engineering.
111 citations,
August 1998 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” μ-opiate receptors in skin cells may affect skin health and healing.
 November 2015 in “European Journal of Inflammation”
November 2015 in “European Journal of Inflammation” Cicatricial alopecia, a permanent hair loss condition, is mainly caused by damage to specific hair follicle stem cells and abnormal immune responses, with gene regulator PPAR-y and lipid metabolism disorders playing significant roles.
 2 citations,
June 2001 in “American Journal of Pathology”
2 citations,
June 2001 in “American Journal of Pathology” The document concludes that understanding how hair follicles naturally die and regenerate is important for insights into organ development and could impact health and disease treatment.
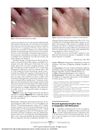 9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology”
9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology” Sunlight exposure improved a patient's skin condition, and there may be a link between a certain disease and skin growths; a leukemia treatment caused changes in hair color and growth.
 66 citations,
May 2021 in “Science Advances”
66 citations,
May 2021 in “Science Advances” Different scaffold patterns improve wound healing and immune response in mouse skin, with aligned patterns being particularly effective.
 29 citations,
May 2020 in “npj Regenerative Medicine”
29 citations,
May 2020 in “npj Regenerative Medicine” Immune cells help regulate hair growth, and better understanding this can improve hair loss treatments.
 71 citations,
February 2020 in “Journal of Translational Medicine”
71 citations,
February 2020 in “Journal of Translational Medicine” Progress has been made in skin and nerve regeneration, but more research is needed to improve methods and ensure safety.
 136 citations,
May 2019 in “Cells”
136 citations,
May 2019 in “Cells” Stem cell therapy, particularly using certain types of cells, shows promise for treating hair loss by stimulating hair growth and development, but more extensive trials are needed to confirm these findings.
 21 citations,
March 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
21 citations,
March 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” Immune cells around hair follicles help control hair growth and could be targets for treating hair disorders.
 January 2018 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine”
January 2018 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine” The nucleus is key in controlling skin growth and repair by coordinating signals, gene regulators, and epigenetic changes.
 31 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Science”
31 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Science” MicroRNAs are important for skin health and could be targets for new skin disorder treatments.
 70 citations,
February 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery”
70 citations,
February 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery” Topical drugs and near-infrared light therapy show potential for treating alopecia.
 7 citations,
January 2018 in “Medicinski arhiv”
7 citations,
January 2018 in “Medicinski arhiv” A herbal extract may help treat certain types of hair loss by reducing a specific gene's activity.























