 53 citations,
September 1999 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology”
53 citations,
September 1999 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology” K16 can partially replace K14 but causes hair loss and skin issues.
4 citations,
April 2012 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Krt16-deficient mice help understand skin disorders like PC and FNEPPK.
 51 citations,
February 2009 in “Journal of dermatological science”
51 citations,
February 2009 in “Journal of dermatological science” Pitx2 helps outer root sheath cells differentiate but can't start hair growth on its own.
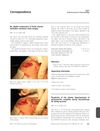 2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Chemotherapy improved a girl's painful foot condition linked to pachyonychia congenita.
 January 2023 in “Frontiers in bioscience”
January 2023 in “Frontiers in bioscience” Artemis protein may help control hair growth and health by influencing cell processes.
 January 2023 in “Open Life Sciences”
January 2023 in “Open Life Sciences” VEGFR-2 activation is likely involved in hair follicle growth, survival, and development.
 July 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
July 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Targeting impaired Nrf2 signaling might help treat hidradenitis suppurativa early on.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Cholecystokinin may help reduce skin inflammation in psoriasis.
 April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Lymphoid-specific helicase (Lsh) is crucial for skin growth, change, and healing after injury.
February 2010 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Activating cAMP and ATP improves hair growth and strength.
 49 citations,
August 2004 in “The FASEB Journal”
49 citations,
August 2004 in “The FASEB Journal” Mice with human skin protein K8 had more skin problems and cancer.
 26 citations,
May 2014 in “BioEssays”
26 citations,
May 2014 in “BioEssays” Using neurohormones to control keratin can lead to new skin disease treatments.
 10 citations,
February 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
February 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Thyrotropin-releasing hormone may help control skin and hair growth and could aid in treating related disorders.
 4 citations,
December 2013 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
4 citations,
December 2013 in “The Journal of Dermatology” A new mutation in the K6b gene caused a girl's late-appearing nail condition.
 211 citations,
April 2018 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology”
211 citations,
April 2018 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology” Keratins are crucial for cell structure, growth, and disease risk.
 109 citations,
September 2011 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics”
109 citations,
September 2011 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics” New treatments targeting specific genes show promise for treating keratin disorders.
 70 citations,
December 2004 in “Differentiation”
70 citations,
December 2004 in “Differentiation” The study identified and characterized new keratin genes linked to hair follicles and epithelial tissues.
 64 citations,
January 2010 in “The FASEB Journal”
64 citations,
January 2010 in “The FASEB Journal” Prolactin affects the production of different keratins in human hair, which could lead to new treatments for skin and hair disorders.
 32 citations,
April 2014 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
32 citations,
April 2014 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Loss of keratin K2 causes skin problems and inflammation.
 3 citations,
June 2022 in “European journal of human genetics”
3 citations,
June 2022 in “European journal of human genetics” A new type of pachyonychia congenita linked to a specific keratin gene mutation was found in two Pakistani families.

Keratin hydrogels from human hair show promise for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
186 citations,
December 2012 in “Current opinion in cell biology” Keratin proteins are increasingly recognized as important for cell health and are linked to many diseases.
27 citations,
November 2007 in “Genomics” Mutations in specific keratin genes cause improper hair structure in mice due to faulty keratin protein assembly.
 January 2024 in “Molecules (Basel. Online)”
January 2024 in “Molecules (Basel. Online)” Juglone from walnut extracts may help repair damaged hair.
115 citations,
August 2014 in “Jo'jig gonghag gwa jaesaeng uihag/Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine” Human hair keratin can be used in many medical applications.
91 citations,
December 2000 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology” Scientists successfully created mouse hair proteins in the lab, which are stable and similar to natural hair.
70 citations,
January 2014 in “International review of cell and molecular biology” Keratin proteins are crucial for healthy skin, but mutations can cause skin disorders with no effective treatments yet.
45 citations,
December 2007 in “The FASEB journal” There are two types of stem cells in rodent hair follicles, each with different keratin proteins.
 19 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
19 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The protein p53 directly reduces the production of Keratin 17, a skin and hair protein, in rats with radiation dermatitis.
3 citations,
March 2023 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Keratin protein production in cells is controlled by a complex system that changes with cell type, health, and conditions like injury or cancer.





















