 9 citations,
July 1992 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
9 citations,
July 1992 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Scalp reduction surgery can effectively treat male pattern baldness when tailored to the patient and performed with care to minimize complications.
 5 citations,
July 2000 in “Southern Medical Journal”
5 citations,
July 2000 in “Southern Medical Journal” Male pattern baldness is often genetic and linked to a hormone, with treatments like finasteride and minoxidil being effective for some men.
 1 citations,
February 2017 in “MOJ bioequivalence & bioavailability”
1 citations,
February 2017 in “MOJ bioequivalence & bioavailability” Treating hair loss effectively may require a multi-sided approach, using different treatments together, and topical treatments could be more effective and safer than oral ones.
 November 2024 in “BMC Surgery”
November 2024 in “BMC Surgery” Follicular unit extraction is an effective and minimally invasive treatment for male hair loss.
 July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” The document concludes that understanding hair follicle histology and the hair cycle is crucial for diagnosing alopecia.
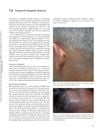 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Temporal triangular alopecia is a lifelong condition with hairless patches on the side of the head that may be present from birth.
 96 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
96 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” The document concludes that adult mammalian skin contains multiple stem cell populations with specific markers, important for understanding skin regeneration and related conditions.
 19 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology”
19 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology” Melanoblasts migrate to the skin using various pathways, and understanding this process could help with skin disease research.
 August 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
August 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” New regenerative therapies show promise for treating hair loss.

Androgenetic alopecia, or hair loss, is caused by a mix of genetics, hormones, and environment, where testosterone affects hair growth and causes hair to become smaller and grow for a shorter time.
 July 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
July 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The research found that male pattern hair loss is mostly genetic and involves hair thinning due to hormonal effects and changes in gene expression.
 47 citations,
September 2016 in “Reviews in endocrine and metabolic disorders”
47 citations,
September 2016 in “Reviews in endocrine and metabolic disorders” The skin's ability to produce hormones is linked to various skin conditions, and better understanding this process could lead to new treatments.
 September 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
September 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine” The scalp fat tissue of men with hair loss shows changes in gene activity that may contribute to their condition.
24 citations,
January 2018 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Androgenetic alopecia is mainly caused by genetic factors and increased androgen activity, leading to hair follicle miniaturization.
 54 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
54 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” DHT, a testosterone byproduct, causes male pattern baldness.
 January 2022 in “Clinical dermatology open access journal”
January 2022 in “Clinical dermatology open access journal” Early-stage Alopecia Areata was effectively treated in less than six months.
 111 citations,
March 2012 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery”
111 citations,
March 2012 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery” Liposomes could improve how skin care products work but are costly and not very stable.
18 citations,
July 2001 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A 12-year-old boy's hair loss and skin issues improved significantly with medication.
 January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” Micropigmentation is a cosmetic tattooing technique for hiding skin issues and creating permanent makeup, but it can have side effects.
18 citations,
June 2010 in “Cell Stress and Chaperones” Heat treatment increases hair loss in certain mice.
AGA is caused by genetics and androgens, treatable with finasteride and minoxidil.
 24 citations,
January 2008 in “KARGER eBooks”
24 citations,
January 2008 in “KARGER eBooks” The document concludes that ongoing research using animal models is crucial for better understanding and treating Alopecia Areata.
 6 citations,
March 1999 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
6 citations,
March 1999 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Scalp biopsies are essential for accurately diagnosing alopecia areata.
 May 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
May 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia in men is genetic and linked to health issues like obesity and heart disease, with treatments including minoxidil, finasteride, and hair transplants.
 February 2024 in “The Open dermatology journal”
February 2024 in “The Open dermatology journal” Alopecia Areata affects people of all ages worldwide, is likely caused by genetic and environmental factors, and can lead to stress and depression, highlighting the need for treatments that address both physical and mental health.
 January 2009 in “Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics”
January 2009 in “Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics” The study suggests that a specific gene variation and higher gene activity are linked to increased baldness in Egyptian men.
69 citations,
April 2010 in “Clinical ophthalmology” Bimatoprost is effective for growing longer, thicker, and darker eyelashes.
 11 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Biological Research”
11 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Biological Research” The study identified 12 potential biomarkers for hair loss and how they affect hair growth.
 April 2024 in “Nigerian Postgraduate Medical Journal”
April 2024 in “Nigerian Postgraduate Medical Journal” Androgenetic alopecia is a common hair loss condition influenced by various factors and linked to psychosocial and cardiovascular issues.
3 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of dermatology & cosmetology” Current alopecia treatments manage symptoms but don't cure, and better treatments are needed.
























