 23 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
23 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Apremilast did not work for treating severe alopecia areata.
March 2019 in “SLAS TECHNOLOGY” New technologies show promise in healing wounds, treating cancer, autoimmune diseases, and genetic disorders.
 October 2023 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
October 2023 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” PPAR-γ may be a key target for treating alopecia areata and other skin conditions.
 15 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of the Formosan Medical Association”
15 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of the Formosan Medical Association” Adalimumab helped control a child's severe eye disease when other treatments failed.
 January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia areata is a reversible, autoimmune-related hair loss that can have significant emotional impact and uncertain treatment effectiveness.
 September 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
September 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Lower vitamin D levels are linked to higher CRP levels in people with a type of hair loss called alopecia areata.
12 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis” Certain IL-18 gene variations may increase the risk of alopecia areata.
 5 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in immunology”
5 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in immunology” Increasing Treg cells in the skin does not cure hair loss from alopecia areata in mice.
 August 2024 in “Current Protocols”
August 2024 in “Current Protocols” The C3H/HeJ mouse model is useful for studying and testing treatments for alopecia areata.
 October 2020 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
October 2020 in “Veterinary Dermatology” New treatments and diagnostic methods for various animal skin conditions showed promising results.
 489 citations,
November 2021 in “Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy”
489 citations,
November 2021 in “Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy” The JAK/STAT pathway is important in cell processes and disease, and JAK inhibitors are promising for treating related conditions.
 80 citations,
April 2018 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine”
80 citations,
April 2018 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine” Lichen Planopilaris and Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia may help us understand hair follicle stem cell disorders and suggest new treatments.
 5 citations,
June 2015 in “Veterinary dermatology”
5 citations,
June 2015 in “Veterinary dermatology” A dog with complete hair loss regrew most hair after treatment, with no relapse after stopping treatment.
 September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Blocking CCR5 can prevent and improve hair loss in alopecia areata.
 September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Scarred skin in lichen planopilaris loses immune cells due to a decrease in a specific protein in skin cells.
5 citations,
March 2016 in “Experimental and molecular pathology” Mice with alopecia areata had wider lymphatic vessels in their skin.
 September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Human hair follicles have a unique way of using energy and might use the Cori cycle; blocking CCR5 could help treat hair loss.
 3 citations,
September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
3 citations,
September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” CBD can either promote or inhibit hair growth depending on the concentration used.
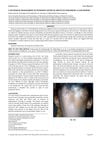 March 2016 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
March 2016 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” Combining OMP with cyclosporine can effectively treat severe alopecia areata in children.
 7 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” T-cell reconstitution after thymus transplantation can cause hair whitening and loss.
 April 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
April 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” The combination of laser and topical steroids is more effective for treating alopecia areata than topical steroids alone.
 19 citations,
September 2002 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
19 citations,
September 2002 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Topical tacrolimus did not regrow hair in alopecia universalis patients.
20 citations,
March 2019 in “Case Reports in Dermatology” IL-17 inhibitors for psoriasis may cause unexpected hair loss.
 4 citations,
January 2013 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
4 citations,
January 2013 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Some patients with Alopecia Areata experience itch due to immune cells and enzymes that cause itching.
 January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” The document explains various skin conditions and their treatments.
 13 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
13 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The laser comb did not improve hair regrowth in mice with alopecia areata.
98 citations,
March 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology” Damaging mutations in NFKB2 cause a severe and distinct form of primary immunodeficiency with early-onset and often ACTH-deficiency.
 62 citations,
June 2015 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
62 citations,
June 2015 in “The Journal of Dermatology” People with alopecia areata have more Th17 cells and fewer Treg cells, which may be key to the condition's development.
 7 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic surgery”
7 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic surgery” Hair transplantation can successfully treat stubborn alopecia areata.
13 citations,
March 2014 in “Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis” Higher MIF levels in alopecia areata patients suggest it could be a treatment target and disease predictor.
























