 306 citations,
April 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
306 citations,
April 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” The skin has a complex immune system that is essential for protection and healing, requiring more research for better wound treatment.
 69 citations,
September 2006 in “Human Reproduction”
69 citations,
September 2006 in “Human Reproduction” Women with PCOS have fewer activated T cells in their ovarian follicles, which might affect fertility.
 90 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy”
90 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy” Lichen planopilaris is a chronic, scarring hair loss condition with no definitive cure, requiring accurate diagnosis and treatment to manage symptoms.
 49 citations,
April 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
49 citations,
April 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Despite progress in treatment, the exact cause of Alopecia areata is still unknown.
 December 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
December 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)” M-CSF-stimulated myeloid cells can cause alopecia areata in mice.
5 citations,
July 2020 in “Recent patents on inflammation & allergy drug discovery” Childhood Alopecia Areata causes hair loss and requires varied treatments, with psychological support being crucial.
 66 citations,
May 2021 in “Science Advances”
66 citations,
May 2021 in “Science Advances” Different scaffold patterns improve wound healing and immune response in mouse skin, with aligned patterns being particularly effective.
 253 citations,
April 2014 in “Drugs”
253 citations,
April 2014 in “Drugs” Teriflunomide helps reduce multiple sclerosis symptoms and is safe for most patients.
 April 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Both induced and spontaneous AA lymphocytes can cause alopecia areata in mice.
16 citations,
April 2014 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” A patient lost all their hair while on rheumatoid arthritis medication.
 June 2023 in “Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)”
June 2023 in “Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)” Inflammation in hair follicles is a key risk factor for developing common baldness.
 14 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
14 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology” UVA1-light therapy successfully treated a child's skin condition, mycosis fungoides.
August 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia may be caused by an autoimmune reaction and hormonal imbalance.
 19 citations,
February 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
19 citations,
February 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” CD3+ T-cell presence is a reliable marker to tell apart alopecia areata from pattern hair loss.

Alopecia areata, a type of hair loss, may be passed through T cells and has genetic links, while treatments vary in effectiveness. Male pattern baldness can be treated with finasteride and is influenced by androgens in hair follicles.
September 2021 in “Eureka: Health Sciences” Androgenetic alopecia in women may be improved by targeting oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis.
 84 citations,
March 2004 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
84 citations,
March 2004 in “Veterinary Dermatology” Cyclosporin is effective in treating dog skin diseases and has fewer side effects compared to other treatments.
December 2019 in “Global pharmaceutical sciences review” New treatments for alopecia are being explored due to the limitations of current options.

Alopecia Areata is treated with drugs and therapies to reduce inflammation and immune response.
57 citations,
May 1980 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Langerhans cells are crucial for skin immunity and allergic reactions.

Wound healing is complex and requires more research to enhance treatment methods.
 April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” People with hair loss have low zinc levels; zinc supplements and laser therapy may help.
 2 citations,
August 2015 in “Journal of dermatology”
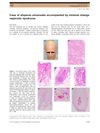
2 citations,
August 2015 in “Journal of dermatology” A possible link exists between minimal change nephrotic syndrome and complete hair loss.
 September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Researchers developed a 3D skin model with its own immune and blood vessel cells to better understand skin health and disease.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” COVID-toes show a unique immune response over time, different from vaccine-related chilblains.
 9 citations,
April 2021 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
9 citations,
April 2021 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Unconventional lymphocytes are important for quick immune responses and healing of skin and mucosal barriers.
 5 citations,
July 1991 in “Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -)”
5 citations,
July 1991 in “Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -)” Immunosuppressive therapy helps manage autoimmune diseases but carries risks like infection and potential for malignancy.
 7 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of comparative pathology”
7 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of comparative pathology” CD8+ T cells play a key role in graft-versus-host disease in certain mice models.
 41 citations,
February 2001 in “Current pharmaceutical design”
41 citations,
February 2001 in “Current pharmaceutical design” Current and future treatments for alopecia areata focus on immunosuppression, immunomodulation, and protecting hair follicles.
 18 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology”
18 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” Certain immune cells contribute to severe hair loss in chronic alopecia areata, with Th17 cells possibly having a bigger impact than cytotoxic T cells.
























