 1 citations,
March 2023 in “Aggregate”
1 citations,
March 2023 in “Aggregate” A new hydrogel with micronized amnion helps achieve better, scar-free skin healing.
The hydrogel helps skin heal faster and better than a commercial dressing by creating a protective environment and supporting new blood vessel and hair growth.
 10 citations,
April 2023 in “Acta biomaterialia”
10 citations,
April 2023 in “Acta biomaterialia” New hydrogel dressing with antibiotic speeds up burn healing and skin regeneration.
24 citations,
September 2020 in “Pharmaceutics” Lidocaine-loaded microparticles effectively relieve pain and fight bacteria in wounds.
 10 citations,
February 2023 in “Colloids and surfaces. A, Physicochemical and engineering aspects”
10 citations,
February 2023 in “Colloids and surfaces. A, Physicochemical and engineering aspects” Adding 1 mg/ml of graphene oxide to egg white protein wound dressings improves antibacterial properties and supports skin repair.
 68 citations,
March 2019 in “Advanced Healthcare Materials”
68 citations,
March 2019 in “Advanced Healthcare Materials” Advanced hydrogel systems with therapeutic agents could greatly improve acute and chronic wound treatment.
 November 2023 in “Indian journal of surgery”
November 2023 in “Indian journal of surgery” Platelet-rich gel is an effective treatment for healing scalp wounds with exposed skull.
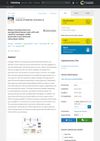 6 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Materials Chemistry B”
6 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Materials Chemistry B” The dressing generates hydrogen sulfide to help heal wounds faster by reducing inflammation and promoting cell growth.
83 citations,
September 2021 in “Advanced functional materials” The DNA hydrogel helps heal diabetic wounds by absorbing fluids, warming, sticking to tissue, killing bacteria, and aiding tissue and hair regrowth.
 47 citations,
March 2017 in “Materials Science and Engineering: C”
47 citations,
March 2017 in “Materials Science and Engineering: C” Human amniotic membrane helps heal skin wounds faster and with less scarring.
 24 citations,
September 2018 in “Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine”
24 citations,
September 2018 in “Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine” Hyaluronic acid-based HA2 hydrogel helps heal skin wounds better with less scarring.
 21 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery”
21 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery” Negative pressure wound therapy is effective for skin grafts in cats.
20 citations,
August 2005 in “The Journal of laboratory and clinical medicine” Mice with damaged skin or hair follicles are more susceptible to anthrax infection.
61 citations,
April 2023 in “Bioactive Materials” Microneedles are effective for painless drug delivery and promoting wound healing and tissue regeneration.
 59 citations,
February 2021 in “Advanced Functional Materials”
59 citations,
February 2021 in “Advanced Functional Materials” The silk fibroin-based hydrogel shows promise for treating melanoma and healing infected wounds by killing tumor cells and bacteria, and supporting skin recovery.
1 citations,
April 2014 in “Journal of the American Geriatrics Society” Diagnosing mycosis fungoides, a rare skin cancer, is difficult in elderly adults and requires careful examination to avoid mistaking it for less serious skin conditions.
6 citations,
January 2018 in “Advances in experimental medicine and biology” Researchers created artificial human skin using special cells, which could help treat skin conditions like albinism and vitiligo.
6 citations,
March 2023 in “Materials” The GNP crosslinked scaffold with antibacterial coating is effective for rapid wound healing and infection prevention.
 January 2020 in “Acta Scientiae Veterinariae”
January 2020 in “Acta Scientiae Veterinariae” Hydrocolloid dressings significantly improved healing of a dog's third-degree burn.
 3 citations,
January 2022 in “Biomaterials Science”
3 citations,
January 2022 in “Biomaterials Science” The dressing can track joint movement and speed up healing of joint wounds.
 1 citations,
December 2022 in “̒Ulūm-i dārūyī”
1 citations,
December 2022 in “̒Ulūm-i dārūyī” The new wound dressing with minoxidil and dexamethasone could speed up healing and reduce scarring in rats.
14 citations,
November 2019 in “Mediators of inflammation” IL-6 from stem cells helps repair skin and grow hair.
17 citations,
December 2013 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The treatment improved hair color in most vitiligo patients without major side effects.
16 citations,
February 2019 in “Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine” Researchers created a rat model to study skin damage caused by radiation, which could help develop new treatments.
 5 citations,
January 2018 in “PubMed”
5 citations,
January 2018 in “PubMed” Biodegradable microneedle patches help topical steroids work better for prurigo nodularis.
 1 citations,
July 2024 in “International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology (IJISRT)”
1 citations,
July 2024 in “International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology (IJISRT)” Stopping steroids and providing supportive care improved the patient's Cushing Syndrome symptoms and ulcers.
 67 citations,
February 1983 in “The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology”
67 citations,
February 1983 in “The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology” Vigilon, a new wound dressing, promotes faster and better healing with less pain.
 1 citations,
February 2004
1 citations,
February 2004 Skin diseases are common and can significantly affect people's lives; better outcome measures and ethical clinical trials are needed to improve dermatology care.
 10 citations,
May 2009 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
10 citations,
May 2009 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Technique effectively reconstructs large scalp defects with minimal hair loss and visible scarring.
 3 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders”
3 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” Hair loss can occur about 4 weeks after scalp surgery but usually grows back within 3 months without treatment.




















