 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Telogen effluvium is a common hair loss condition where many hairs enter the resting phase, often not noticeable until significant loss occurs, and treatment focuses on the underlying cause.
 50 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of investigational allergology & clinical immunology”
50 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of investigational allergology & clinical immunology” Dupilumab is being tested for many new skin, respiratory, and gastrointestinal conditions.
 March 2022 in “Berkala Ilmu Kesehatan Kulit dan Kelamin/Berkala ilmu kesehatan kulit dan kelamin (Periodical of dermatology and venerology)”
March 2022 in “Berkala Ilmu Kesehatan Kulit dan Kelamin/Berkala ilmu kesehatan kulit dan kelamin (Periodical of dermatology and venerology)” Touching cats can increase the risk of getting a fungal scalp infection, especially in boys and kids over 5.
 113 citations,
August 2016 in “Mycopathologia”
113 citations,
August 2016 in “Mycopathologia” New topical antifungals and delivery systems are improving treatment for fungal skin infections, but patient education and prevention are key.
 March 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences”
March 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Zinc, copper, and iron are important for skin health and may help diagnose skin diseases.
 23 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in dermatology”
23 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in dermatology” Alopecia areata involves immune response and gene changes affecting hair loss.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” The document says a skin condition called alopecia areata causes hair loss and stress, and is treated with strong skin creams, injections, or other therapies, but treatment success varies.
 3 citations,
October 2007 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
3 citations,
October 2007 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Hair ages due to various factors and treatments like minoxidil and finasteride can help, but more research and better public awareness are needed.
 126 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology”
126 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology” Oxidative stress contributes to hair graying and loss as we age.
 17 citations,
January 2011 in “Skin Research and Technology”
17 citations,
January 2011 in “Skin Research and Technology” Hair from people with seborrheic dermatitis is thicker scaled, more damaged, and thinner than healthy hair, and atomic force microscopy can help monitor the condition.
 49 citations,
July 2021 in “Nutrients”
49 citations,
July 2021 in “Nutrients” Eating healthy, exercising, and taking certain supplements can help manage Polycystic Ovary Syndrome symptoms.

Early identification of lupus through skin signs and blood tests is crucial in India.
 11 citations,
January 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology”
11 citations,
January 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology” Polarized microscopy is a quick and free method to correctly identify types of hair loss.
 4 citations,
June 2013 in “The Journal of Rheumatology”
4 citations,
June 2013 in “The Journal of Rheumatology” The document concludes that various findings in rheumatology offer insights into disease severity, treatment responses, and potential risks in medication, with some limitations due to unspecified participant numbers.
 80 citations,
April 2006 in “Clinical Interventions in Aging”
80 citations,
April 2006 in “Clinical Interventions in Aging” Minoxidil and Finasteride are effective for male baldness; more research is needed for hair aging treatments.
January 2025 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Male pattern baldness worsens with age and can be treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride, but side effects and personalized care are important.
 18 citations,
July 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
18 citations,
July 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Volatile organic compounds can cause inflammation and increase the risk of autoimmune diseases.
 19 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
19 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Ultraviolet rays damage hair, smoking may cause hair loss, and good nutrition is important for hair health, but genetics mainly decide hair thickness.
 13 citations,
September 2019 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
13 citations,
September 2019 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Early treatment of EPDS can improve outcomes and reduce recurrence risk.
 3 citations,
July 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
3 citations,
July 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” A woman's hair loss, resembling an autoimmune condition, improved after treatment, but requires ongoing checks due to potential serious associations.
 1 citations,
November 2022 in “Cureus”
1 citations,
November 2022 in “Cureus” Some COVID-19 patients have skin issues, with men, ICU patients, and those on multiple antibiotics at higher death risk; in-person skin checks by dermatologists are more effective.
 15 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
15 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia and androgenetic alopecia may be related, with a possible shared cause.
 61 citations,
September 2010 in “Genomics”
61 citations,
September 2010 in “Genomics” The study found that immune responses disrupt hair growth cycles, causing hair loss in alopecia areata.
2 citations,
June 2024 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Alopecia Areata can affect nails, often improving on its own, but JAK inhibitors may help.
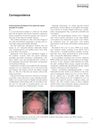 12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A woman developed a scalp condition from using minoxidil, which improved with a different treatment but left scarring.
3 citations,
September 2021 in “BioEssays” Dandruff might be caused by changes in how hair follicles naturally release oils and an immune response to this imbalance.
 August 2022 in “International Journal of Health Sciences (IJHS) (En línea)”
August 2022 in “International Journal of Health Sciences (IJHS) (En línea)” Oxidative stress is important in causing alopecia areata.
 150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology”
150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology” The document concludes that more research is needed to better understand and treat primary cicatricial alopecias, and suggests a possible reclassification based on molecular pathways.
1 citations,
December 2023 in “Molecules/Molecules online/Molecules annual” JAK inhibitors show promise for treating various skin diseases.
 December 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
December 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” These specific gene polymorphisms are not linked to Alopecia Areata in Egyptians.


























