August 2020 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)” Finasteride, at doses of 5mg or higher, may negatively affect male fertility by reducing the expression of certain genes involved in sperm production.
 June 2021 in “Archives of Advances in Biosciences”
June 2021 in “Archives of Advances in Biosciences” Finasteride reduces sperm count and quality and alters hormone levels in mice.
 58 citations,
January 2003 in “Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin”
58 citations,
January 2003 in “Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin” Bombax ceiba stem bark extracts can lower blood pressure, but high doses can be toxic and lethal.
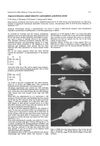 2 citations,
September 1980 in “Experientia”
2 citations,
September 1980 in “Experientia” Polyethylene alanine caused hair loss in young lab animals but not in adults, with hair regrowth occurring within 20 days.
 25 citations,
February 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
25 citations,
February 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Blocking SCD1 in the skin with XEN103 shrinks sebaceous glands in mice.
 October 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
October 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Blocking both main energy pathways can stop hair follicle stem cell-induced skin cancer growth.
 5 citations,
July 2003 in “Drug Development Research”
5 citations,
July 2003 in “Drug Development Research” Fluridil promotes hair growth safely and effectively for androgenetic alopecia.
 January 2024 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
January 2024 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” The gene Ascl4 is not necessary for the development of hair, teeth, or mammary glands.
 7 citations,
January 2018 in “Indian Journal of Pharmacology”
7 citations,
January 2018 in “Indian Journal of Pharmacology” Algerian Carthamus caeruleus L plant has anti-inflammatory properties, heals wounds effectively, and may help with hair growth.
 37 citations,
January 2002 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
37 citations,
January 2002 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Apple extract called procyanidin B-2 was found to greatly increase hair growth.
 23 citations,
January 2001 in “International journal of toxicology”
23 citations,
January 2001 in “International journal of toxicology” St. John's Wort extract and oil safety in cosmetics is unclear; more data needed on photosensitization, toxicity, and human irritation.
 12 citations,
December 2021 in “Aging”
12 citations,
December 2021 in “Aging” A new painless method to collect hair follicles helps study DNA damage and aging.
 2 citations,
October 2015 in “Human Gene Therapy”
2 citations,
October 2015 in “Human Gene Therapy” The congress highlighted new gene therapy techniques and cell transplantation methods for treating diseases.
 165 citations,
September 2003 in “Toxicology and applied pharmacology”
165 citations,
September 2003 in “Toxicology and applied pharmacology” Blocking COX, especially COX-2, in the skin can reduce inflammation and pain and may help prevent skin cancer.
 43 citations,
February 2013 in “Developmental dynamics”
43 citations,
February 2013 in “Developmental dynamics” Foxi3 expression in developing teeth and hair is controlled by the ectodysplasin pathway.
 17 citations,
August 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
17 citations,
August 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Fluridil safely promotes hair growth in men with androgenetic alopecia.
 10 citations,
January 1985 in “Elsevier eBooks”
10 citations,
January 1985 in “Elsevier eBooks” Active oxygen species might be involved in skin tumor growth, but their exact role is unclear.
 7 citations,
July 2013 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
July 2013 in “International Journal of Dermatology” No link found between Coxsackie viruses and pemphigus.
 March 2023 in “Enciclopédia Biosfera”
March 2023 in “Enciclopédia Biosfera” Finasteride effectively treats BPH but requires continuous use to maintain benefits.
 August 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
August 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Fluridil safely promotes hair growth in men with androgenetic alopecia.
Diphenyl cresyl phosphate has low toxicity but can harm the liver, kidneys, adrenal glands, and testicles at high doses.
 95 citations,
July 2010 in “Genes & development”
95 citations,
July 2010 in “Genes & development” Notch/CSL signaling controls hair follicle differentiation through Wnt5a and FoxN1.
142 citations,
March 2019 in “Molecules/Molecules online/Molecules annual” Cannabinoids may help treat various skin conditions.
 14 citations,
January 2016 in “Experimental and molecular pathology”
14 citations,
January 2016 in “Experimental and molecular pathology” Giving immune serum from vaccinated mice to mice without T cells prevents infection and tumor growth.
68 citations,
December 2010 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” HOXC13 is essential for hair and nail development by regulating Foxn1.
 6 citations,
August 2022 in “Science immunology”
6 citations,
August 2022 in “Science immunology” Foxn1 gene regulation is crucial for thymus development but not for hair growth.
 1 citations,
December 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
1 citations,
December 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Keeping β-catenin levels high in mammary cells disrupts their development and branching.
 5 citations,
July 1999 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
5 citations,
July 1999 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Proteolytic enzymes damage hair follicles by detaching stem cells.
 127 citations,
December 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
127 citations,
December 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Mice hair growth patterns get more complex with age and can change with events like pregnancy or injury.
 86 citations,
October 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology”
86 citations,
October 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology” The Foxn1 gene mutation causes hairlessness and immune system issues, and understanding it could lead to hair growth disorder treatments.

























