1 citations,
April 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Conflicting findings in androgenic alopecia are likely due to biopsy location, hair diameter diversity, and hair follicle miniaturization.
 22 citations,
March 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
22 citations,
March 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Many treatments for hair loss lack proper testing and FDA approval, so their effectiveness is uncertain.
 30 citations,
January 2000 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
30 citations,
January 2000 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Finasteride and minoxidil are effective FDA-approved treatments for androgenetic alopecia.
 29 citations,
December 1998 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
29 citations,
December 1998 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” New treatments for hair loss show promise, especially finasteride for men and a stronger minoxidil formula.
 3 citations,
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
3 citations,
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” AGA is a genetic, hormonal hair loss treated with finasteride, minoxidil, and supplements, but new compounds are being developed.
2 citations,
March 2011 in “Hair transplant forum international” Female pattern hair loss involves hair follicles shrinking, influenced by hormones like melatonin and prolactin.
 January 2003 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2003 in “Springer eBooks” Androgenic alopecia is a type of hair loss that's partly inherited and can be due to hormonal imbalance.
 17 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
17 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The conclusion is that accurate diagnosis of different types of hair loss requires careful examination of tissue samples and understanding of clinical symptoms.
 4 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology”
4 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology” AGA causes hair loss through follicle miniaturization and hair cycle changes; regrowth depends on anagen initiation in kenogen follicles.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” AGA is a common hair loss affecting both genders, treated with various therapies to promote regrowth and slow thinning.
 30 citations,
May 2016 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
30 citations,
May 2016 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Hair loss in women links to inflammation around hair follicles.
 8 citations,
April 2020 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
8 citations,
April 2020 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Minoxidil, finasteride, and low-level laser light therapy are effective FDA-approved treatments for hair loss.
 73 citations,
November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
73 citations,
November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Some women with common hair loss may develop permanent hair loss.
 January 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications”
January 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications” Injecting a peptide-hyaluronic acid mix improved hair growth in men with hair loss and was safe.
 1 citations,
January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks” Finasteride increases hair count and improves hair growth with low risk of side effects.
 77 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
77 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia involves genetics, hormones, and can be treated with medications or surgery.
 23 citations,
May 2009 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
23 citations,
May 2009 in “International Journal of Dermatology” AR gene not major factor in female hair loss; different from male hair loss.
 3 citations,
April 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
3 citations,
April 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Male hair loss is caused by inactive hair follicle stem cells.
 June 2024 in “Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal”
June 2024 in “Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal” Multi-omics techniques help understand the molecular causes of androgenetic alopecia.
 August 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
August 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Men with early hair loss may have a higher risk of enlarged prostate and possibly prostate cancer due to shared hormonal factors.
 September 2022 in “Polish Hyperbaric Research”
September 2022 in “Polish Hyperbaric Research” Some treatments for hair loss, like finasteride, biotin, and minoxidil, can be effective, but their success varies by individual case.
 45 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
45 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Trichoscopy is better than trichogram for diagnosing female hair loss.
 27 citations,
April 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
27 citations,
April 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss involves immune responses, inflammation, and disrupted signaling pathways.
 May 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
May 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss caused by longer latent hair cycle and sudden miniaturization, not gradual follicle size reduction.
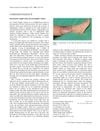 1 citations,
May 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
May 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss caused by longer latent hair cycle and sudden miniaturization, not gradual follicle size reduction.
 April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The research found genes that may protect certain scalp cells from hair loss.
 February 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
February 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Hair loss in Androgenetic Alopecia is caused by genetics, aging, and lifestyle, leading to hair follicle shrinkage and related health risks.
AGA is caused by genetics and androgens, treatable with finasteride and minoxidil.
 90 citations,
June 2006 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
90 citations,
June 2006 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis of different types of hair loss requires careful examination of hair and scalp tissue, considering both clinical and microscopic features.
 29 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
29 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Hair disorders are caused by a complex mix of biology, genetics, hormones, and environmental factors, affecting hair growth and leading to conditions like alopecia.


























