 July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ”
July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ” Alopecia areata is a hair loss condition caused by immune factors and can be treated with JAK inhibitors.
52 citations,
September 2014 in “Nature medicine” JAK inhibitors might help treat alopecia areata.
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Blocking JAK1 or JAK3 helps reverse hair loss in a mouse model of alopecia areata.
 3 citations,
February 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
3 citations,
February 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical tofacitinib cream may help treat certain hair loss conditions with fewer risks.
 1 citations,
January 2024 in “Curēus”
1 citations,
January 2024 in “Curēus” Upadacitinib significantly improved a man's severe scalp condition when other treatments failed.
 June 2024 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
June 2024 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Upadacitinib may effectively treat resistant lichen planopilaris.
29 citations,
December 2019 in “Expert review of clinical pharmacology” JAK inhibitors are a promising new treatment for hair loss and nail problems in alopecia areata.
 3 citations,
August 2020 in “Case Reports in Dermatology”
3 citations,
August 2020 in “Case Reports in Dermatology” Tofacitinib treatment significantly improved a patient's psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and alopecia universalis.
 June 2023 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
June 2023 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Baricitinib was effective in treating severe and very severe alopecia areata after 52 weeks.
 1 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Tofacitinib may help regrow hair in severe alopecia areata, but results differ greatly between people.
 238 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
238 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Tofacitinib is effective and safe for severe hair loss, but full regrowth is less likely after 10 years of hair loss.
 37 citations,
October 2017 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
37 citations,
October 2017 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Oral tofacitinib shows promise in treating atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata, but only slight improvement in vitiligo.
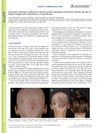 24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Tofacitinib helped a young woman's severe hair loss and arthritis but not her plaque psoriasis.
 March 2018 in “Suez Canal University Medical Journal”
March 2018 in “Suez Canal University Medical Journal” New drugs targeting the JAK-STAT pathway show promise for treating inflammatory skin diseases.
 April 2024 in “JEADV clinical practice”
April 2024 in “JEADV clinical practice” Upadacitinib significantly improved both rheumatoid arthritis and alopecia areata in a patient.
 May 2024 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
May 2024 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Tofacitinib is an effective and safe treatment for alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
June 2023 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
1 citations,
June 2023 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Baricitinib helps regrow hair in severe alopecia areata but has side effects like infections and headaches.
 6 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of autoimmunity”
6 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of autoimmunity” JAK inhibitors like tofacitinib may effectively treat Alopecia Areata.
 11 citations,
October 2018 in “Pediatric dermatology”
11 citations,
October 2018 in “Pediatric dermatology” Leflunomide and anthralin may effectively treat severe alopecia areata.
 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Alopecia Areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with limited and variable treatment effectiveness.
 November 2017 in “Asian journal of pharmaceutical and clinical research”
November 2017 in “Asian journal of pharmaceutical and clinical research” Three compounds from Dadap leaves may help treat hair loss.
 January 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
January 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Baricitinib helped most teenagers with severe hair loss regrow hair and had mild side effects.
 8 citations,
May 2017 in “Singapore Medical Journal”
8 citations,
May 2017 in “Singapore Medical Journal” A Korean woman with complete hair loss regrew her hair after taking tofacitinib, with no side effects.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Aging reduces skin cell renewal and defense against germs due to TGFbeta, but blocking TGFbeta could help restore these functions.
2 citations,
February 2023 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Baricitinib effectively improved both atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata symptoms in a patient.
 16 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
16 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Ruxolitinib may help treat hair loss by reducing inflammation, promoting hair growth signals, and protecting hair follicle immunity.
6 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Alopecia areata involves complex immune and genetic factors, with potential treatment targets identified, but more research is needed.
 4 citations,
April 2019 in “Cell Stem Cell”
4 citations,
April 2019 in “Cell Stem Cell” Certain immune cells in the skin can stop hair from growing.
14 citations,
April 2021 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Mesenchymal stem cells may help treat hair loss by improving hair cell growth and reducing inflammation.
 290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, influenced by genetics, stress, and diet, and may be prevented by a high soy oil diet.
























