 October 2023 in “Bioactive Materials”
October 2023 in “Bioactive Materials” The new hair loss treatment combining nitric oxide and minoxidil in a special carrier is effective for hair regrowth.
4 citations,
March 2022 in “BioEssays” Hydra can help understand human hair follicle microbiomes and develop new skin disease therapies.
 6 citations,
July 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
6 citations,
July 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” Skin can produce blood cells, often due to disease, which might lead to new treatments for skin and blood conditions.
 September 2013 in “Experimental Dermatology”
September 2013 in “Experimental Dermatology” The document concluded that stem cells are crucial for skin repair, regeneration, and may help in developing advanced skin substitutes.
Different genes and pathways are active in yak skin and hair cells, affecting hair growth and immune responses.

The hydrogel significantly improves healing in diabetic wounds.
 15 citations,
September 2007 in “Cell & tissue research/Cell and tissue research”
15 citations,
September 2007 in “Cell & tissue research/Cell and tissue research” Embryonic and adult stem cells are valuable for improving skin grafts and cell therapy.
 21 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
21 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Rats can't grow new hair follicles after skin wounds, unlike mice, due to differences in gene expression and response to WNT signaling.
 4 citations,
June 2022 in “BioMed Research International”
4 citations,
June 2022 in “BioMed Research International” Using mesenchymal stem cells or their exosomes is safe for COVID-19 patients and helps improve lung healing and oxygen levels.
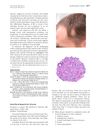
The man has Temporal Triangular Alopecia, a stable, non-scarring hair loss condition best treated with hair transplantation.
3 citations,
November 2011 in “Small GTPases” Researchers found that hair follicle stem cells can become squamous cell carcinoma due to Ras activation, which could lead to new treatments.
 9 citations,
February 2022 in “Nature communications”
9 citations,
February 2022 in “Nature communications” Rare changes in the KRT82 gene are linked to a higher risk of Alopecia Areata.
665 citations,
April 2016 in “Nature communications” Blocking specific proteins can help remove aging cells and might treat age-related diseases and promote hair growth.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair loss patterns differ between males and females due to 5 master regulators and JAK-STAT signaling affects hair growth.
 6 citations,
January 1998 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
6 citations,
January 1998 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Estrogen receptors may not affect mouse hair growth as previously thought, and oxybenzone in sunscreen is stable in sunlight.
 January 2023 in “Advances in reproductive sciences”
January 2023 in “Advances in reproductive sciences” Higher levels of the protein Pannexin-1 may play a role in hair loss in women with PCOS.
 7 citations,
May 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology”
7 citations,
May 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology” Two mouse mutations cause similar hair loss despite different skin changes.
186 citations,
December 2012 in “Current opinion in cell biology” Keratin proteins are increasingly recognized as important for cell health and are linked to many diseases.
 1 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” People respond differently to hair loss treatment with PRP because of individual differences in growth factors from platelets.
 4 citations,
January 2007 in “Australian Veterinary Journal”
4 citations,
January 2007 in “Australian Veterinary Journal” A horse's sudden hair loss was caused by an allergic reaction to a coat conditioning powder.
38 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Aging slows wound healing due to weaker cells and immune response.
134 citations,
July 2020 in “Experimental dermatology” Hair follicles are normally protected from the immune system, but when this protection fails, it can cause hair loss in alopecia areata.
 148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity”
148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease causing patchy hair loss, often with other autoimmune disorders, but its exact causes are unknown.
17 citations,
May 2014 in “Cell transplantation” Genetically modified stem cells from human hair follicles can lower blood sugar and increase survival in diabetic mice.
PRP injections effectively improve hair growth in androgenic alopecia.
 August 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tofacitinib is a potential alternative treatment for alopecia totalis, especially in patients with a shorter duration of the condition and more preserved hair follicles, but the overall response rate is low.
25 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy” New treatments for alopecia areata may target specific immune cells and pathways involved in hair loss.
 12 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
12 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Hair loss in autoimmune blistering skin diseases varies and may regrow with disease control.
 June 2022 in “Scientific Reports”
June 2022 in “Scientific Reports” Prevelex, a polyampholyte, can create a cell-repellent coating on microdevices, which can be useful in biomedical applications like hair follicle regeneration.
84 citations,
February 2015 in “Experimental Dermatology” PPARγ is crucial for skin health but can have both beneficial and harmful effects.


















