 55 citations,
March 2015 in “Carcinogenesis”
55 citations,
March 2015 in “Carcinogenesis” WNT10A helps esophageal cancer cells spread and keep renewing themselves.
 13 citations,
October 2010 in “Pharmacogenomics”
13 citations,
October 2010 in “Pharmacogenomics” Researchers found that most genes affecting drug responses are not fully covered by commercial SNP chips, suggesting the need for more comprehensive tools to optimize drug selection based on genetics.
 57 citations,
March 2019 in “Immunity”
57 citations,
March 2019 in “Immunity” The document concludes that the skin's immune system is complex, involving interactions with hair follicles, nerves, and microbes, and can protect or cause disease, offering targets for new treatments.
 18 citations,
July 2014 in “Molecular Medicine Reports”
18 citations,
July 2014 in “Molecular Medicine Reports” UVB radiation changes the levels of certain microRNAs in skin cells, which may affect cell survival and hair growth.
 13 citations,
September 2019 in “EBioMedicine”
13 citations,
September 2019 in “EBioMedicine” sPLA2-IIA increases growth in hair follicle stem cells and cancer cells, suggesting it could be targeted for hair growth and cancer treatment.
 10 citations,
August 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
10 citations,
August 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” Decorin helps hair cells grow and move, and keeps hair growth phase going in mice.
 7 citations,
November 2022 in “Communications biology”
7 citations,
November 2022 in “Communications biology” Keratin injections can promote hair growth by affecting hair-forming cells and tissue development.
 7 citations,
October 2019 in “Annals of palliative medicine”
7 citations,
October 2019 in “Annals of palliative medicine” New targeted cancer drugs can cause skin side effects, and managing them requires patient education and timely care.
 December 2023 in “Communications biology”
December 2023 in “Communications biology” Targeting the HEDGEHOG-GLI1 pathway could help treat keloids.
 July 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
July 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” Androgens like testosterone affect skin health and can lead to conditions such as acne and hair loss, with various treatments available.
35 citations,
January 2018 in “Vitamins and hormones” DHEA affects various tissues by interacting with multiple receptors and can be converted into sex hormones.
43 citations,
January 2016 in “Cellular physiology and biochemistry” Epidermal Growth Factor helps hair follicle cells grow and move by activating a specific cell signaling pathway.
3 citations,
May 2016 in “Dermatopathology” Lrig1 could be a marker for advanced sebaceous carcinoma.
 2 citations,
May 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
2 citations,
May 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” The TRPV3 ion channel is important for skin and hair health and could be a target for treating skin conditions.
 1 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
March 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” ZD1839, a cancer drug, can cause mild skin rashes that are treatable without stopping the medication.
1 citations,
December 2012 in “Journal of dermatological science” Combining ficlatuzumab and gefitinib can cause severe scarring hair loss.
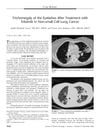 12 citations,
November 2006 in “Journal of thoracic oncology”
12 citations,
November 2006 in “Journal of thoracic oncology” A cancer patient's eyelashes grew excessively without other common side effects after taking the cancer drug erlotinib.
 July 2023 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
July 2023 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Some lung cancer patients treated with EGFR inhibitors may develop a hair loss condition similar to folliculitis decalvans.
 October 2021 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology”
October 2021 in “International journal of basic and clinical pharmacology” Excessive eyelash growth from erlotinib may indicate positive tumor response and help treat madarosis.
 June 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
June 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Adverse events in lung cancer treatments increase fear, anxiety, and depression, with newer therapies causing fewer side effects.
 5 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
5 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” The document concludes that individualized treatment for malignant epithelial tumors is necessary and more research on metastatic squamous cell carcinoma treatments is needed.
 5 citations,
January 2021 in “Dermatology Online Journal”
5 citations,
January 2021 in “Dermatology Online Journal” An 84-year-old man developed a rare scalp condition from a cancer drug but continued treatment as it was otherwise well tolerated.
32 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Skin reactions from cancer treatments might predict how well the treatments work.
 16 citations,
October 2014 in “Oral surgery, oral medicine, oral pathology and oral radiology”
16 citations,
October 2014 in “Oral surgery, oral medicine, oral pathology and oral radiology” Keratoacanthoma comes from hair follicle cells.
26 citations,
February 2015 in “Pediatric blood & cancer” Targeted anticancer therapies in children often cause skin side effects like rash and dry skin.
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Y27632 increases cell growth through EGFR signaling, not ROCK1/2.
 January 2021 in “Journal of Cancer Therapy”
January 2021 in “Journal of Cancer Therapy” Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors are effective against cancer but can cause skin, digestive, and blood side effects, including hair loss.
 November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Cancer treatment drugs can cause permanent hair loss by damaging hair follicle stem cells, but a specific inhibitor might reverse this effect.
April 2012 in “Cancer research” Blocking mTORC1 may help prevent skin cancer by stopping the growth of certain skin stem cells.
 138 citations,
February 2007 in “European journal of cancer”
138 citations,
February 2007 in “European journal of cancer” EGFR inhibitors often cause skin problems and other side effects, but these are usually reversible and can be managed to keep patients comfortable.






















