 January 2024 in “Vestnik oftalʹmologii”
January 2024 in “Vestnik oftalʹmologii” Stopping minoxidil and using prostaglandin analogues improved the man's eye condition.
 January 2024 in “Pan African Medical Journal”
January 2024 in “Pan African Medical Journal” Non-scarring hair loss is common in lupus patients and can be diagnosed with specific hair and tissue tests.
 July 2023 in “Biomolecules”
July 2023 in “Biomolecules” The circadian clock plays a key role in hair growth and its disruption can affect hair regeneration.
 October 2021 in “Cosmoderma”
October 2021 in “Cosmoderma” Hair loss can be managed with treatments like minoxidil, finasteride, and others, but there are still gaps in effectiveness and off-label usage is increasing.
82 citations,
March 2013 in “PLoS ONE” Vemurafenib causes skin side effects similar to RASopathies, requiring regular skin checks and UVA protection.
11 citations,
July 2018 in “AJGP” Low-dose oral minoxidil effectively reduces hair loss in women with female pattern hair loss.
 January 2024 in “Asian Journal of Medical Sciences”
January 2024 in “Asian Journal of Medical Sciences” Dermoscopes help tell FPHL apart from other hair loss types and can detect it early by identifying specific patterns.
 November 2023 in “International Journal of Trichology”
November 2023 in “International Journal of Trichology” Trichoscopic features help diagnose and assess female pattern hair loss severity, with inflammation playing a key role.
 November 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
November 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Injecting a person's own fat into their scalp may help regrow hair and improve hair thickness in different types of hair loss.
 October 2023 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
October 2023 in “The Journal of Dermatology” The HSVS-A is an effective tool for quickly screening hair shedding in Asian women.
 January 2018 in “Surgical and Cosmetic Dermatology”
January 2018 in “Surgical and Cosmetic Dermatology” The method is effective for evaluating hair loss treatments quickly and affordably.
 4 citations,
January 2019 in “PubMed”
4 citations,
January 2019 in “PubMed” Patterned hair loss in women is linked to hormonal imbalances and biochemical changes, and should be evaluated for underlying health issues.
 February 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
February 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Hair loss in Androgenetic Alopecia is caused by genetics, aging, and lifestyle, leading to hair follicle shrinkage and related health risks.
 September 2023 in “Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -)”
September 2023 in “Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -)” About 61% of women who had COVID-19 experienced hair loss afterward.
 July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” The document concludes that understanding hair follicle histology and the hair cycle is crucial for diagnosing alopecia.
 March 2022 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
March 2022 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Botulinum Neurotoxin-A can treat acne, oily skin, rosacea, hair loss, prevent scars, relieve nerve pain, reduce excessive sweating, and manage psoriasis, but more trials are needed to confirm its effectiveness.

Androgenetic alopecia is not linked to higher risks of hypertension or hyperaldosteronism.
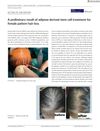 April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Stem cell treatment improved hair density in female hair loss patient.
 129 citations,
October 2007 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
129 citations,
October 2007 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Over one-third of women experience hair loss, with female-pattern hair loss being most common, and treatments include minoxidil and possibly hair transplantation.
 54 citations,
February 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
54 citations,
February 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss in women may have causes other than hormones.
 46 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
46 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Female pattern hair loss diagnosed by scalp appearance, treated with combined therapies and targeted approaches.
 29 citations,
April 2004 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
29 citations,
April 2004 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Women with female pattern hair loss often underestimate how severe it is.
 22 citations,
October 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
22 citations,
October 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Fisetin, a type of polyphenol, may help hair grow by increasing certain protein activities in cells.
 15 citations,
February 2014 in “BMC Research Notes”
15 citations,
February 2014 in “BMC Research Notes” The X5 Hairlaser might help treat male hair loss, but more research is needed.
 14 citations,
January 2006 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
14 citations,
January 2006 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Alopecia areata can look like frontal fibrosing alopecia, making diagnosis hard.
 1 citations,
January 2001
1 citations,
January 2001 Micrografting is the most effective surgical method for permanent hair restoration.

Accurate diagnosis and tailored treatments are crucial for managing hair loss in humans and animals.
 January 2011 in “Web journal anti-aging medicine/Anti-aging medicine”
January 2011 in “Web journal anti-aging medicine/Anti-aging medicine” KGS1 tablets improved skin and hair health.
 November 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
November 2015 in “Springer eBooks” Hair loss treated with minoxidil, finasteride, laser/light, hair transplant, and scalp prostheses; more research needed for skin of color.
 229 citations,
August 2002 in “Experimental Gerontology”
229 citations,
August 2002 in “Experimental Gerontology” AGA causes hair loss by shrinking hair follicles due to DHT binding, and can be treated with finasteride and minoxidil.




























