The estrogen receptor pathway controls hair growth cycles and affects skin cell growth.
Stem cell treatments show promise for hair loss but need more research.
January 2022 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine” iPSCs could help develop treatments for hair loss.
October 2021 in “Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open” Adipose-derived stem cells may help treat hair loss.
October 2021 in “QJM: An International Journal of Medicine” ADSC injections improve hair density, thickness, and reduce inflammation in female pattern hair loss.
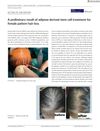 April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Stem cell treatment improved hair density in female hair loss patient.
April 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology” T-cell patterns in skin help distinguish alopecia areata from androgenetic alopecia.
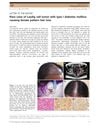 August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology”
August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology” Woman with diabetes had hair loss due to rare ovarian tumor; surgery improved hair growth.
January 2019 in “Journal of Clinical Dermatology” The hair tonic improved hair growth and thickness without severe side effects.
 September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The protein aPKCλ is crucial for keeping hair follicle stem cells inactive and for hair growth and regeneration.
 April 2013 in “Dermatology and therapy”
April 2013 in “Dermatology and therapy” Crescina treatment improves hair resistance and reduces hair loss.
 773 citations,
August 2017 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
773 citations,
August 2017 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” The secretions of mesenchymal stem cells could be used for healing without using the cells themselves.
 320 citations,
December 2018 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
320 citations,
December 2018 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Changing how mesenchymal stromal cells are grown can improve their healing abilities.
 305 citations,
June 2012 in “Nature”
305 citations,
June 2012 in “Nature” Hair regeneration needs dynamic cell behavior and mesenchyme presence for stem cell activation.
245 citations,
October 2015 in “Nature medicine” Hair follicle-derived IL-7 and IL-15 are crucial for maintaining skin-resident memory T cells and could be targeted for treating skin diseases and lymphoma.
 211 citations,
April 2013 in “Development”
211 citations,
April 2013 in “Development” More dermal papilla cells in hair follicles lead to larger, healthier hair, while fewer cells cause hair thinning and loss.
 209 citations,
March 1989 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
209 citations,
March 1989 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Interferon alfa-2a is effective for treating cutaneous T cell lymphoma but has significant side effects.
 179 citations,
July 2016 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology”
179 citations,
July 2016 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology” Epigenetic changes control how adult stem cells work and can lead to diseases like cancer if they go wrong.
176 citations,
February 2006 in “Cancer Research” Patched1 helps prevent tumors by controlling cell growth.
173 citations,
July 1995 in “Biochemical and biophysical research communications” Male hormones promote hair cell growth by using a growth factor from nearby skin cells.
 168 citations,
August 2009 in “EMBO molecular medicine”
168 citations,
August 2009 in “EMBO molecular medicine” Epidermal stem cells are diverse and vary in activity, playing key roles in skin maintenance and repair.
153 citations,
April 1998 in “Current Biology” The risk of skin tumors becoming malignant depends on the specific skin cell type affected.
 133 citations,
September 2013 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology”
133 citations,
September 2013 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology” Different types of stem cells and their environments are key to skin repair and maintenance.
114 citations,
March 2010 in “Zebrafish” PROTO1 and PROTO2 protect against hearing damage.
 107 citations,
December 2003 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
107 citations,
December 2003 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Interferon, especially alfa interferon, is an effective treatment for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma with manageable side effects.
 96 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
96 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” The document concludes that adult mammalian skin contains multiple stem cell populations with specific markers, important for understanding skin regeneration and related conditions.
 95 citations,
May 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
95 citations,
May 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Androgens block hair growth by disrupting cell signals; targeting GSK-3 may help treat hair loss.
 95 citations,
July 2010 in “Genes & development”
95 citations,
July 2010 in “Genes & development” Notch/CSL signaling controls hair follicle differentiation through Wnt5a and FoxN1.















