27 citations,
August 2021 in “Journal of Autoimmunity” Human dermal γδT-cells respond to stress in hair follicles, contributing to hair loss.
 January 2021 in “Our Dermatology Online”
January 2021 in “Our Dermatology Online” Oral tofacitinib successfully treated total body hair loss in one patient.
2 citations,
May 2020 in “JAAD case reports” Ruxolitinib can cause a delayed skin reaction on the nose.
 March 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
March 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” Upadacitinib may effectively treat alopecia areata without side effects.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition, with various treatments showing mixed effectiveness and no guaranteed cure.
 11 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
11 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Stopping JAK inhibitor treatment for hair loss can lead to worse hair loss than before the treatment.
 37 citations,
October 2017 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
37 citations,
October 2017 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Oral tofacitinib shows promise in treating atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata, but only slight improvement in vitiligo.
16 citations,
June 2018 in “JAAD case reports” A JAK inhibitor improved both severe hair loss and chronic skin disease in one patient.
 24 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology”
24 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology” Tofacitinib helped regrow hair in patients with alopecia, with few side effects.
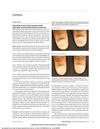 41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology”
41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology” Tofacitinib citrate improved nail dystrophy and pain in patients with alopecia universalis without causing side effects.
39 citations,
March 2017 in “Dermatologic clinics” UV light can help stimulate the growth of new pigment cells from hair follicles in people with vitiligo.
75 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Alopecia areata can be triggered by specific immune cells without genetic or environmental factors.
139 citations,
October 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The nail matrix has a reduced immune response, protecting it from autoimmunity.
 December 2024 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
December 2024 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Minoxidil shows promise for alopecia areata, but more research is needed before it can be recommended as a primary treatment.
 27 citations,
December 2015 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
27 citations,
December 2015 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Diphencyprone helped most patients with alopecia areata regrow some hair.
18 citations,
June 2010 in “Cell Stress and Chaperones” Heat treatment increases hair loss in certain mice.
 1 citations,
May 2021 in “Cell Host & Microbe”
1 citations,
May 2021 in “Cell Host & Microbe” Skin bacteria, specifically Streptococcus and Staphylococcus, help in hair regrowth after skin injury and speed up wound healing.
14 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” New therapies for alopecia areata show potential but need more research.
 January 2025 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
January 2025 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Potential therapeutic targets for scarring hair loss are identified.
 4 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
4 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Hair loss treatment caused more hair loss in a man.

Tofacitinib may effectively treat hair loss and improve symptoms in autoimmune conditions like alopecia areata and Sjögren's syndrome, but long-term treatment might be necessary.
 June 2020 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
June 2020 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Tiny particles from skin cells can help activate hair growth.
 70 citations,
February 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery”
70 citations,
February 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery” Topical drugs and near-infrared light therapy show potential for treating alopecia.
 2 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders”
2 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders” Early onset, severe types, nail changes, family history, and body hair loss worsen alopecia areata prognosis; sticking to treatment helps.
 October 2023 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
October 2023 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” PPAR-γ may be a key target for treating alopecia areata and other skin conditions.
 1 citations,
November 2022 in “Cureus”
1 citations,
November 2022 in “Cureus” Some COVID-19 patients have skin issues, with men, ICU patients, and those on multiple antibiotics at higher death risk; in-person skin checks by dermatologists are more effective.
 April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The research identified unique metabolic activities in immune cells associated with hair loss in Alopecia Areata.
 5 citations,
June 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
5 citations,
June 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology” A certain medication improved severe itching in a boy with liver and bowel disease by reducing histamine levels, suggesting a new treatment target.
1 citations,
August 2023 in “Biomolecules” Certain immune-related proteins are higher in people with alopecia and their healthy relatives, hinting at a genetic link.
22 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research” Certain genetic variations in IL18 may increase the risk of alopecia areata in Koreans.



















