 March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements”
March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements” Gene variation affects prostate issues and hair loss.
 March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements”
March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements” CEC levels may be a useful marker for predicting prostate cancer progression.
 21 citations,
February 2021 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology”
21 citations,
February 2021 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” Hormones affect prostate health and disease, with certain hormone imbalances linked to prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia.
[object Object]  6 citations,
January 1996 in “Endocrine-related Cancer”
6 citations,
January 1996 in “Endocrine-related Cancer” Combining flutamide and finasteride can reduce prostate weight and tumor growth, potentially benefiting treatments needing optimal DHT inhibition.
 1 citations,
December 2013 in “Urological Science”
1 citations,
December 2013 in “Urological Science” A man developed male breast cancer after four years of finasteride treatment for an enlarged prostate.
 97 citations,
November 1986 in “Journal of Steroid Biochemistry”
97 citations,
November 1986 in “Journal of Steroid Biochemistry” Antiandrogens affect androgen-dependent body functions and are used for various medical conditions, with some risks like fetus feminization, but new forms like 17α-propylmesterolone show promise for acne without systemic effects.
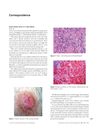 October 2010 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
October 2010 in “International Journal of Dermatology” An 86-year-old man with prostate cancer was diagnosed with a rare, low-grade breast cancer and underwent surgery but declined additional hormone therapy.
 11 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
11 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Hair loss gene linked to prostate issues.
 75 citations,
January 2014 in “Korean Journal of Urology”
75 citations,
January 2014 in “Korean Journal of Urology” 5α-reductase inhibitors can cause sexual problems, higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer, and depression.
 3 citations,
March 2005 in “The Journal of urology/The journal of urology”
3 citations,
March 2005 in “The Journal of urology/The journal of urology” Dutasteride may help shrink prostate cancer tumors.
 29 citations,
July 2009 in “BJU international”
29 citations,
July 2009 in “BJU international” Blocking DHT production more strongly may help control advanced prostate cancer and improve quality of life.

Deleting Smad4 and PTEN genes in mice causes rapid, invasive stomach cancer.

Deleting Smad4 and PTEN genes in mice causes rapid, invasive forestomach cancer.
 57 citations,
January 1986 in “The Prostate”
57 citations,
January 1986 in “The Prostate” The document suggests that targeting the hormone DHT could be a more effective treatment for prostate cancer than targeting testosterone.
1 citations,
August 2022 in “Veterinary medicine and science” The main prostate diseases in dogs are benign growth, infections, and cancer, with various treatments ranging from drugs to surgery, but cancer treatments have limited success.
 88 citations,
February 2008 in “Journal of Medicinal Chemistry”
88 citations,
February 2008 in “Journal of Medicinal Chemistry” Scientists made the first metal-based compounds from a nonsteroidal antiandrogen drug, which showed potential in fighting both hormone-dependent and independent prostate cancer cells.
 51 citations,
May 2013 in “The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology”
51 citations,
May 2013 in “The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology” Certain drugs that block specific enzymes can help treat prostate diseases.
 30 citations,
June 1988 in “Journal of Steroid Biochemistry”
30 citations,
June 1988 in “Journal of Steroid Biochemistry” Flutamide combined with an LHRH agonist effectively inhibits prostate growth, suggesting it could treat prostate cancer.
 16 citations,
September 1964 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
16 citations,
September 1964 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” New compounds can block testosterone effects in rats and might help treat conditions like prostate cancer and acne.
 March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements”
March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements” The document concludes that a new biosensor can efficiently detect prostate cancer cells and that standardized referrals help find significant cancers effectively.
 72 citations,
January 2003 in “American Journal of Pathology”
72 citations,
January 2003 in “American Journal of Pathology” A protein called CBP is found in prostate cancer and can increase the effectiveness of certain prostate cancer treatments.
 32 citations,
May 2006 in “The Journal of Urology”
32 citations,
May 2006 in “The Journal of Urology” Using finasteride with TIP extends time off period for prostate cancer patients.
 17 citations,
January 2016 in “American Journal of Epidemiology”
17 citations,
January 2016 in “American Journal of Epidemiology” Men with male pattern baldness have a higher risk of dying from prostate cancer.
50 citations,
April 2010 in “Biology direct” Low androgen levels might delay prostate cancer but could lead to more aggressive, therapy-resistant cancers.
 20 citations,
March 2005 in “Current Medicinal Chemistry”
20 citations,
March 2005 in “Current Medicinal Chemistry” New compounds show promise for treating hair loss, enlarged prostate, and prostate cancer, with some being more effective and having different side effects than current treatments.
 93 citations,
February 2009 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences”
93 citations,
February 2009 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences” 5α‐reductase isozymes are crucial for prostate development and health, and targeting them can help prevent and treat prostate issues.
 8 citations,
January 1986 in “Journal of hepatology”
8 citations,
January 1986 in “Journal of hepatology” Men with liver cancer have higher levels of a specific testosterone byproduct in their liver and blood, despite overall lower male hormone levels.
[object Object]  March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements”
March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements” Blood tests for tumor cells could improve prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment; hair loss severity linked to a gene affecting prostate conditions.
 237 citations,
December 2001 in “Urology”
237 citations,
December 2001 in “Urology” Blocking the enzyme 5α-reductase can shrink the prostate and help treat enlarged prostate issues.
 28 citations,
January 2003 in “Urologic oncology”
28 citations,
January 2003 in “Urologic oncology” Suppressing certain hormones might help prevent prostate cancer.



























