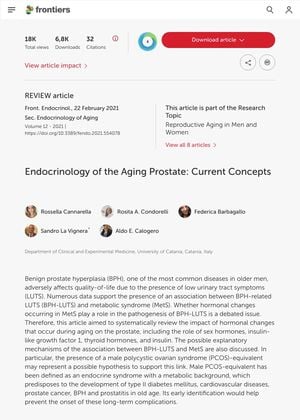
Endocrinology of the Aging Prostate: Current Concepts
February 2021
in “
Frontiers in Endocrinology
”
estrogen insulin-like growth factor IGF thyroid hormones estrogen receptor alpha ERbeta IGF1 benign prostatic hyperplasia BPH triiodothyronine T3 metabolic syndrome hyperinsulinemia dyslipidemia androgen-targeted therapies castration resistance obesity metformin polycystic ovary syndrome PCOS androgenetic alopecia
TLDR Hormones affect prostate health and disease, with certain hormone imbalances linked to prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia.
The 2021 document "Endocrinology of the Aging Prostate: Current Concepts" discussed the role of hormones in prostate health and disease, particularly focusing on estrogen, insulin-like growth factor (IGF), and thyroid hormones. The document cited studies showing that estrogen receptor alpha drives proliferation in prostate carcinoma and that loss of ERbeta expression is a common step in estrogen-dependent tumor progression. IGF deficiency was linked to metabolic syndrome and IGF1 was related to prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Increased serum triiodothyronine (T3) levels were found in men with prostate cancer and BPH. The document also highlighted the link between metabolic syndrome and BPH, with hyperinsulinemia and dyslipidemia as risk factors. The research suggested that androgen-targeted therapies could induce changes in prostate cancer cells, contributing to the development of castration resistance. Obesity and hyperinsulinemia were identified as risk factors for prostate cancer. The potential use of metformin in improving the survival of diabetic prostate cancer patients was discussed. The document also suggested a possible genetic link between polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and androgenetic alopecia, indicating that a male equivalent of PCOS might exist. Androgenetic alopecia was suggested as an early marker of BPH and prostate cancer, but more research is needed to confirm these associations.