9 citations,
June 2023 in “Cells” Certain natural and synthetic compounds may help treat inflammatory skin diseases by targeting a specific signaling pathway.
 7 citations,
October 2020 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
7 citations,
October 2020 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Some skin, hair, and nail supplements can be toxic, interact with medications, affect lab tests, and may increase cancer risk.
2 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology” Natural products may help treat skin inflammation from abnormal adrenal hormones.
2 citations,
March 2021 in “Reproduction” Finasteride may affect male fertility by interfering with specific sperm signaling.
 1 citations,
April 2023 in “Biomolecules”
1 citations,
April 2023 in “Biomolecules” Fermented papaya and mangosteen in hair care products helped prevent hair loss and improve hair thickness.
 1 citations,
April 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
1 citations,
April 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” New CRISPR/Cas9 variants and nanotechnology-based delivery methods are improving cancer treatment, but choosing the best variant and overcoming certain limitations remain challenges.
 1 citations,
February 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
1 citations,
February 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Melatonin, the sleep hormone, can help treat skin conditions like dermatitis, hyperpigmentation, and scalp disorders, and may also aid in skin aging prevention and regeneration. However, it's not recommended for asthma due to its pro-inflammatory effect.
 December 2024 in “Nutrients”
December 2024 in “Nutrients” Skin, hair, and nail changes can help detect eating disorders early.
 September 2023 in “International Journal of Trichology”
September 2023 in “International Journal of Trichology” Oral Vitamin D can improve hair density and reduce hair loss in Telogen Effluvium patients.
 August 2023 in “Processes”
August 2023 in “Processes” Fermenting Dendrobium officinale with Lactobacillus reuteri CCFM8631 increases its skin care benefits.
August 2023 in “Diagnostics” Ultra-high-frequency ultrasound effectively evaluates the impact of hyaluronic acid fillers in reducing nasolabial fold wrinkles over time.

Plant-based compounds can improve wound dressings and skin medication delivery.
Different types of sun exposure damage skin cells and immune cells, with chronic exposure leading to more severe and lasting damage.
1 citations,
January 2010 in “Biophysical journal” Hair fluorescence intensity can measure radiation exposure effectively.
 6 citations,
October 2007 in “Medical Hypotheses”
6 citations,
October 2007 in “Medical Hypotheses” Male pattern baldness might have evolved to help protect against prostate cancer by increasing UV radiation on the scalp.
March 2007 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Hair with more melanin resists weather damage better.
31 citations,
February 1999 in “Dermatologic surgery” Sun exposure after laser hair removal can cause skin darkening, which is hard to treat and requires avoiding UV light.
 30 citations,
November 1996 in “Archives of Dermatology”
30 citations,
November 1996 in “Archives of Dermatology” UV rays can cause a type of hair loss known as telogen alopecia.
 April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Caffeine can protect scalp hair follicles from damage caused by UV radiation.
December 2009 in “Expert review of dermatology” Vitamin D may help protect against nonmelanoma skin cancer.
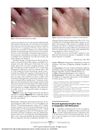 9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology”
9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology” Sunlight exposure improved a patient's skin condition, and there may be a link between a certain disease and skin growths; a leukemia treatment caused changes in hair color and growth.
5 citations,
October 2003 in “PubMed” Chemical treatments and light exposure damage hair proteins.
 9 citations,
September 2009 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
9 citations,
September 2009 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” UV light causes skin color loss in bald areas; wear a cap and use sunscreen.
13 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of photochemistry and photobiology. B, Biology” UV radiation increases protein loss from hair and reduces hair protein quality.
 December 2024 in “Cell Communication and Signaling”
December 2024 in “Cell Communication and Signaling” Fat tissue vesicles protect skin from UV damage better than stem cell vesicles.
144 citations,
December 2017 in “Pigment cell & melanoma research” Melasma is now considered a skin aging disorder caused by sun exposure in people with a genetic tendency, which impacts treatment and prevention approaches.
 10 citations,
July 2022 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
10 citations,
July 2022 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Melasma's causes include genetics, sun exposure, hormones, and oxidative stress, and understanding these can help create better treatments.
 6 citations,
August 1993 in “Archives of Dermatology”
6 citations,
August 1993 in “Archives of Dermatology” The study found that polymorphous light eruption varies among patients and can be distinguished from benign summer light eruption by the time it takes for symptoms to appear after sun exposure.
 August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Infant skin cells may be less capable of repairing UV-induced DNA damage than adult cells.
 August 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
August 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Increasing type 17 collagen reduces aging signs in skin cells caused by UV light.

















