 3 citations,
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
3 citations,
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Activating TLR3 improves the healing and immune properties of periodontal ligament stem cells.
 3 citations,
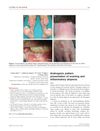
January 2010 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
3 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Many people diagnosed with androgenic alopecia might actually have hidden scarring or inflammation.
2 citations,
December 2023 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Wound healing is greatly affected by the types of bacteria present, which can either help or hinder the process.
 2 citations,
January 2022 in “Experimental Dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2022 in “Experimental Dermatology” GDNF signaling helps in hair growth and skin healing after a wound.
 2 citations,
July 2021 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
2 citations,
July 2021 in “Dermatologic Therapy” A woman's hair loss after COVID-19 was likely due to a mix of pressure-induced alopecia and acute telogen effluvium.
 2 citations,
December 2019 in “Archives of Craniofacial Surgery”
2 citations,
December 2019 in “Archives of Craniofacial Surgery” Using a method of stretching skin multiple times can help cover large bald spots on the scalp, but it takes a long time and isn't good for kids.
 2 citations,
January 2013 in “Hair therapy & transplantation”
2 citations,
January 2013 in “Hair therapy & transplantation” Hair transplants can be a treatment for scarring hair loss if there's good blood flow and no active disease.
 1 citations,
September 2023 in “ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering”
1 citations,
September 2023 in “ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering” Human hair keratin hydrogels show promise for use in regenerative medicine.
1 citations,
April 2023 in “Scientific Reports” Self-assembling RADA16-I hydrogels with bioactive peptides significantly improve wound healing.
 1 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
1 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Using a 30°-sapphire blade at a lower angle causes the least injury in hair transplants.
 1 citations,
May 2019 in “Cytotherapy”
1 citations,
May 2019 in “Cytotherapy” New Australian advertising rules improved stem cell marketing practices but further regulation is needed for consumer safety.
 1 citations,
November 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
November 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that transplantology has evolved with improved techniques and materials, making transplants more successful and expanding the types of transplants possible.
 1 citations,
January 2018
1 citations,
January 2018 Improve burn patients' appearance and function using various techniques, teamwork, and psychological support.

The conclusion is that closing scalp wounds is possible, but restoring hair without donor material is still a major challenge.
 1 citations,
December 2006 in “Burns”
1 citations,
December 2006 in “Burns” New therapies for burn wounds show promise in reducing pain, infection risk, and improving healing and physical outcomes.
 1 citations,
November 2002 in “Neurosurgery Clinics of North America”
1 citations,
November 2002 in “Neurosurgery Clinics of North America” The article concludes that cranial reconstruction should aim for the best aesthetic result, using various techniques tailored to individual needs and conditions.
 August 2024 in “Nature Communications”
August 2024 in “Nature Communications” Softer hydrogels help wounds heal better with less scarring.
 July 2024 in “Gene & Protein in Disease”
July 2024 in “Gene & Protein in Disease” Exosome therapy shows promise for treating skin conditions and improving wound healing.
 May 2024 in “Journal of drug delivery science and technology”
May 2024 in “Journal of drug delivery science and technology” Exosomes show promise for treating skin diseases and improving skin regeneration.
 December 2023 in “Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan IPA”
December 2023 in “Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan IPA” PRP heals pockmarked skin better than salmon DNA serum.
 November 2023 in “Journal of Drugs in Dermatology”
November 2023 in “Journal of Drugs in Dermatology” Hypochlorous acid spray improves wound healing and reduces redness and itching in hair transplant surgery.
 November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The article concludes that creating a detailed map of normal human skin at the single-cell level is important.
 August 2023 in “International journal of medical science and clinical research studies”
August 2023 in “International journal of medical science and clinical research studies” PRP therapy helps heal pediatric surgical wounds faster and with fewer scars but needs more research for safety and cost.
 June 2023 in “JAAD Case Reports”
June 2023 in “JAAD Case Reports” A man had a rare skin cancer that looked like a bald spot.
August 2022 in “Tissue Engineering Part A” Advancements in skin treatment and wound healing include promising gene therapy, 3D skin models, and potential new therapies.
 April 2022 in “Anti-cancer agents in medicinal chemistry”
April 2022 in “Anti-cancer agents in medicinal chemistry” Some existing medicines show promise as safe treatments to protect against the side effects of radiation therapy.
 January 2022 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Research”
January 2022 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Research” Choose the simplest, most fitting scalp reconstruction method for each patient's unique needs.
 January 2022 in “Biocell”
January 2022 in “Biocell” Mesenchymal stem cells and their secretions might help treat chronic skin inflammation in atopic dermatitis.
 January 2022 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine”
January 2022 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine” New biofabrication technologies could lead to treatments for hair loss.
 June 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
June 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Platelet-rich Plasma Gel may help treat en coup de sabre scleroderma, improving symptoms and skin quality with minimal side effects.



























