 47 citations,
March 2022 in “Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology”
47 citations,
March 2022 in “Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology” Changes in skin microbes play a role in some skin diseases and could lead to new treatments.
 3 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
3 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Caffeine shows promise for treating some types of hair loss, but more research is needed.
 10 citations,
April 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy”
10 citations,
April 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy” Calcipotriol works almost as well as clobetasol for mild to moderate alopecia areata with fewer side effects.
3 citations,
June 2021 in “Frontiers in genetics” The protein STAT3 slows down cell growth by blocking the FST gene, which affects hair development in sheep.
 23 citations,
August 2018 in “Biochimica and biophysica acta. Molecular and cell biology of lipids”
23 citations,
August 2018 in “Biochimica and biophysica acta. Molecular and cell biology of lipids” Different sPLA2 enzymes affect immunity, skin and hair health, reproduction, and may be potential targets for therapy.
 January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Acne can appear or persist in adulthood due to hormonal changes, external factors, or substance use, and requires appropriate treatment.
February 2023 in “PLOS ONE” Caizhixuan hair tonic helps treat hair loss by promoting hair growth and improving hair follicles.
 3 citations,
May 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
3 citations,
May 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” Young HS patients often have other physical and mental health issues, and research on HS covers a wide range of topics including genetics, triggers, treatments, and the need for more data.
 11 citations,
November 2012 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
11 citations,
November 2012 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Genetic factors affect hair loss, and molecular testing may help predict, diagnose, and treat it.
 February 2022 in “Global academic journal of medical sciences”
February 2022 in “Global academic journal of medical sciences” People with alopecia areata have much lower Vitamin-D levels than healthy individuals.

Alopecia areata patients show increased inflammation and OX40 activation, suggesting a new treatment target.
 45 citations,
October 2014 in “Stem cell research & therapy”
45 citations,
October 2014 in “Stem cell research & therapy” Modified rat stem cells on a special scaffold improved blood vessel formation and wound healing in skin substitutes.
 January 2024 in “Frontiers in endocrinology”
January 2024 in “Frontiers in endocrinology” The study suggests that hypothyroidism may cause alopecia areata.
 4 citations,
April 2023 in “Autoimmunity reviews”
4 citations,
April 2023 in “Autoimmunity reviews” High levels of IL6 and CRP, and low levels of vitamin D, might be indicators of alopecia areata.
 December 2021 in “Revista da Sociedade Portuguesa de Dermatologia e Venereologia”
December 2021 in “Revista da Sociedade Portuguesa de Dermatologia e Venereologia” Imbalance in scalp bacteria can affect hair and scalp health, potentially leading to conditions like hair loss, psoriasis, and dandruff.
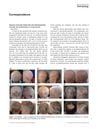 1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A 6-year-old girl with alopecia universalis regrew most of her hair after treatment with simvastatin/ezetimibe, minoxidil, and prednisolone.
 7 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
7 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Less than a quarter of alopecia areata cases were unusual forms or had paradoxical regrowth.
 April 2023 in “Journal of dermatological treatment”
April 2023 in “Journal of dermatological treatment” Ixekizumab successfully treated a rare hair loss condition, leading to complete hair regrowth.
















