 1 citations,
January 2019 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology”
1 citations,
January 2019 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” STAT5 is crucial for hair growth in 3D cultured human dermal papilla cells.
 1 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” PRC1 is essential for proper skin development and stem cell formation by controlling gene activity.
 1 citations,
January 2018 in “Methods in molecular biology”
1 citations,
January 2018 in “Methods in molecular biology” The research found ways to activate melanocyte stem cells for potential treatment of skin depigmentation conditions.
 1 citations,
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” The skin's dermal layer contains true stem cells with diverse functions and interactions that need more research to fully understand.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of nutrition & health”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of nutrition & health” Fish oil improves skin health in people with diabetes and high cholesterol.
 1 citations,
January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that the skin is a complex organ providing protection, sensation, and healing, with challenges in treating conditions like itchiness.
 July 2024 in “Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin”
July 2024 in “Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin” Licorice extract helps hair growth and may treat hair loss.
 January 2024 in “Journal of cellular immunology”
January 2024 in “Journal of cellular immunology” Hair follicle stem cells are important for maintaining healthy skin and interact with many signals.
 August 2023 in “Scientific reports”
August 2023 in “Scientific reports” Human stem cells were turned into cells similar to those that help grow hair and showed potential for hair follicle formation.
 May 2020 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
May 2020 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Researchers found four key stages of cell development that are important for hair growth and shedding in cashmere goats.
 April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Eating grape powder may reduce the severity of skin allergy symptoms.
 April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Calcium signals and SHH guide the direction of feather growth in chicken skin.
 September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The Siah1 and Siah2 genes are active in mouse skin development and hair growth, especially right after birth.
 September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Aging causes sweat glands to shrink and move upward, leading to less elastic skin and more wrinkles.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” PRC1 influences skin stem cell development by both turning genes on and off, affecting hair growth and skin cell types.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Removing the Crif1 gene in mouse skin disrupts skin balance and hair growth.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Applying pseudoceramide improved skin and hair health.
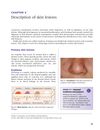
The document explains different types of skin lesions and their characteristics, causes, and related conditions.
 August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” DHT reduces a cell's ability to promote hair growth, while 3D culture without DHT improves it.
 March 2015 in “Plastic and reconstructive surgery”
March 2015 in “Plastic and reconstructive surgery” Human skin has multiple layers and functions, with key roles in protection, temperature control, and appearance.
 September 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
September 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” TNC+ fibroblasts play a key role in skin inflammation by interacting with T cells.
 March 2012 in “Pathy's Principles and Practice of Geriatric Medicine”
March 2012 in “Pathy's Principles and Practice of Geriatric Medicine” Older adults often have skin problems due to aging, and treating these conditions requires attention to both physical and mental health.
 February 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
February 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” ROS may affect hair loss related to hormones.
 1039 citations,
February 2009 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology”
1039 citations,
February 2009 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology” Skin stem cells are crucial for maintaining and repairing the skin and hair, using a complex mix of signals to do so.
 788 citations,
February 2007 in “Nature”
788 citations,
February 2007 in “Nature” The document concludes that skin stem cells are important for hair growth and wound healing, and could be used in regenerative medicine.
 610 citations,
April 2014 in “Nature Reviews Immunology”
610 citations,
April 2014 in “Nature Reviews Immunology” The document concludes that understanding how the skin's immune system and inflammation work is complex and requires more research to improve treatments for skin diseases.
 401 citations,
January 2013 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii”
401 citations,
January 2013 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii” The paper concludes that understanding melanocyte development can help in insights into skin diseases and melanoma diversity.
 277 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
277 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” The skin's layers protect, sense, and regulate the body's internal balance, but can be prone to cancer.
 276 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
276 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The document concludes that mouse models are helpful but have limitations for skin wound healing research, and suggests using larger animals and genetically modified mice for better human application.
 268 citations,
April 2009 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics”
268 citations,
April 2009 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics” Niosomes improve minoxidil skin delivery for hair loss treatment.






























