 1 citations,
August 2022 in “Molecules”
1 citations,
August 2022 in “Molecules” Prunus mira kernels contain components that can promote hair growth in mice.
 October 1961 in “Archives of Dermatology”
October 1961 in “Archives of Dermatology” Reassurance is important for postpartum hair shedding as it likely won't cause complete baldness.
 62 citations,
December 2013 in “Aaps Journal”
62 citations,
December 2013 in “Aaps Journal” Squarticles effectively deliver hair growth drugs to follicles and dermal papilla cells.
[object Object] 5 citations,
January 2021 in “PeerJ” Elephant tail-hair can show past stress levels, matching times when stressful events happened.
 3 citations,
May 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
3 citations,
May 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” A new treatment using nanoparticles can effectively prevent and reduce hair loss caused by chemotherapy.
 January 2009 in “Side effects of drugs annual”
January 2009 in “Side effects of drugs annual” Some drugs can cause serious side effects like heart issues and nervous system problems, but certain drugs for Parkinson's and overactive bladder may be safer, though they still have some common side effects.
 6 citations,
May 1987 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
6 citations,
May 1987 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Syphilis patients showed abnormal hair root changes, with no difference between primary and secondary stages.
 3 citations,
January 2000
3 citations,
January 2000 Some alternative therapies for vitiligo show promise but need more research.

Some plant-based ingredients may help with hair growth and care, but more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
 53 citations,
October 2012 in “The FASEB Journal”
53 citations,
October 2012 in “The FASEB Journal” Bimatoprost, a glaucoma medication, may also help treat hair loss.
[object Object] January 2020 in “JAAD case reports” Systemic mastocytosis may cause a type of hair loss called cicatricial alopecia.
61 citations,
October 2011 in “Experimental dermatology” Scalp itching is common and hard to diagnose due to the complex nerve structure of the scalp.
February 2023 in “PLOS ONE” Caizhixuan hair tonic helps treat hair loss by promoting hair growth and improving hair follicles.
 10 citations,
March 2015 in “PubMed”
10 citations,
March 2015 in “PubMed” Scalp micropigmentation, a cosmetic tattoo technique, is a promising non-surgical treatment for hair and scalp deformities, despite potential complications.
 20 citations,
January 2015 in “Polish Journal of Pathology”
20 citations,
January 2015 in “Polish Journal of Pathology” Reflectance confocal microscopy is a useful, non-invasive tool for diagnosing some skin diseases, with potential for future improvements.
 October 2022 in “Boletín médico del Hospital infantil de México/Boletín médico del Hospital Infantil de México”
October 2022 in “Boletín médico del Hospital infantil de México/Boletín médico del Hospital Infantil de México” The patient has a rare skin condition that shows features of two known disorders.
1 citations,
March 2006 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” The woman's forehead lesion was caused by ointment use and resolved with treatment.

The skin is a complex barrier for drug penetration, but understanding its structure and interactions can improve drug delivery methods.
 28 citations,
December 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
28 citations,
December 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” Some medications might reverse gray hair, especially those that reduce inflammation or stimulate pigment production, and vitamin B might help.
 21 citations,
June 2004 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
21 citations,
June 2004 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Most skin diseases in Hajjah, Yemen, were dermatitis, infections, and acne, influenced by local socioeconomic and environmental factors.
 21 citations,
August 2011 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
21 citations,
August 2011 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Looking at skin can help find and treat serious diseases early.
 1 citations,
October 2023 in “Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology”
1 citations,
October 2023 in “Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology” COVID-19 can cause various skin issues, but long-term skin problems are rare.
 44 citations,
October 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
44 citations,
October 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Botulinum toxin has potential for treating various skin conditions and improving wound healing.
 9 citations,
March 2012 in “Experimental dermatology”
9 citations,
March 2012 in “Experimental dermatology” Natural gene therapy shows promise for treating skin disorders like epidermolysis bullosa.
 3 citations,
September 2005 in “Experimental dermatology”
3 citations,
September 2005 in “Experimental dermatology” The cornified envelope is crucial for skin's barrier function and involves key proteins and genetic factors.
 33 citations,
August 2006 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
33 citations,
August 2006 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Pregnancy can cause specific skin conditions that need correct diagnosis and treatment to protect both mother and baby.
 15 citations,
January 2018 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
15 citations,
January 2018 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Skin treatment can lower life quality for patients with skin conditions.
 88 citations,
January 2011 in “Annals of Dermatology”
88 citations,
January 2011 in “Annals of Dermatology” The document concludes that specific itchy skin diseases during pregnancy have varying fetal risks and treatments, including corticosteroids and other medications.
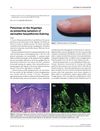 30 citations,
March 2009 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
30 citations,
March 2009 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Red spots on fingertips can be a sign of a skin condition linked to gluten sensitivity, treatable with a gluten-free diet.
 15 citations,
December 2016 in “Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin”
15 citations,
December 2016 in “Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin” The new cream with N-acetyl glucosamine didn't change skin color after 8 weeks.

























