December 2021 in “Journal of V. N. Karazin Kharkiv National University: Series Medicine” The treatment improved hair health in women with androgenetic alopecia.
October 2021 in “Technology transfer: innovative solutions in medicine” The combined treatment improved scalp health in women with early-stage hair loss.
 5 citations,
October 2014 in “Journal of cosmetic and laser therapy”
5 citations,
October 2014 in “Journal of cosmetic and laser therapy” Combining physical dermabrasion with chemical peeling is more effective for skin treatment than chemical peeling alone.
 205 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
205 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Male and female skin differ in many ways, which could lead to gender-specific skin treatments.
 49 citations,
March 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
49 citations,
March 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Using the drugs AMD3100 and Tacrolimus together greatly improves skin healing and hair growth after a deep skin cut by increasing stem cells in the wound.
43 citations,
November 2012 in “Pharmaceutical research” Fractional CO2 laser treatment significantly boosts drug and nanoparticle skin absorption, especially through hair follicles.
 24 citations,
July 2011 in “PubMed”
24 citations,
July 2011 in “PubMed” Thyroid hormones affect skin texture, hair and nail growth, and can cause skin diseases related to thyroid problems.
 18 citations,
June 2017 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America”
18 citations,
June 2017 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” A gene called Gk5 controls lipid production in the skin and affects hair growth.
 2 citations,
July 2017 in “IEEE Photonics Journal”
2 citations,
July 2017 in “IEEE Photonics Journal” The study found that combining SHG and OCT effectively monitors skin wound healing in mice.
 2 citations,
November 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
2 citations,
November 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Epidermal stem cells show promise for future dermatology treatments due to ongoing advancements.
 November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Removing MCPIP1 from myeloid cells in mice leads to hair loss and prevents skin tumors but causes pigmented spots.
 February 2018 in “Trends in Immunology”
February 2018 in “Trends in Immunology” Skin bacteria can help wound healing by activating certain immune cells.
 February 1956 in “Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine”
February 1956 in “Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine” Glycogen levels in mouse skin drop after injury but increase during healing, returning to normal within a month.
 44 citations,
July 2011 in “Dermato-endocrinology”
44 citations,
July 2011 in “Dermato-endocrinology” Thyroid hormone affects skin health, with too little causing rough, pale skin and too much leading to smooth, thin skin, and may also impact wound healing and skin conditions.
37 citations,
January 2006 in “Carcinogenesis” Antizyme slows skin tumor growth by reducing cell growth in mice.
32 citations,
May 2017 in “Lasers in medical science” Radiofrequency treatment helps rejuvenate skin by boosting collagen and blood vessel growth.
December 2024 in “Chinese Chemical Letters” A new topical finasteride gel using nanoparticles shows promise for safe and effective hair regrowth.
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Deleting MPZL3 increases skin oil production and reduces body fat.
The enzyme Dgat1 is essential for healthy hair and skin by controlling retinoid levels.
88 citations,
August 2014 in “PLOS genetics” Syndecan-1 is essential for maintaining skin fat and preventing cold stress.
 16 citations,
September 2018 in “Scientific reports”
16 citations,
September 2018 in “Scientific reports” Scientists created keratinocyte cell lines from human hair that can differentiate similarly to normal skin cells, offering a new way to study skin biology and diseases.
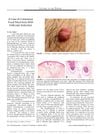 1 citations,
February 2017 in “The American journal of dermatopathology/American journal of dermatopathology”
1 citations,
February 2017 in “The American journal of dermatopathology/American journal of dermatopathology” A man with a skin nodule was diagnosed with a rare skin condition called cutaneous focal mucinosis, which can be confused with other skin cancers.
A new method allows for controlled, long-lasting delivery of retinoic acid through the skin with less inflammation.
 56 citations,
March 2015 in “Cell death and differentiation”
56 citations,
March 2015 in “Cell death and differentiation” Older skin has higher cancer risk due to inflammation and stem cell issues.
 20 citations,
October 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
20 citations,
October 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Some drugs can cause skin and hair color changes, often reversible when the drug is stopped.
 December 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
December 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in the skin helps fat cell development during hair growth and repair.
36 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of controlled release” A new method allows for controlled, long-lasting delivery of retinoic acid through the skin with fewer side effects.
 4 citations,
February 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
4 citations,
February 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The document concludes that a protein involved in hair growth may link to baldness and that more research is needed on its role in hair loss and skin cancer treatments.
2 citations,
January 2014 Improved methods create smaller, more effective gelatin nanoparticles for skin delivery, and new caffeine nanocrystals enhance absorption and effectiveness.
 153 citations,
October 2012 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
153 citations,
October 2012 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” Caffeine in cosmetics may reduce cellulite, protect skin, and stimulate hair growth, but more research is needed on its use and effects.

















