 7 citations,
November 2013 in “Pediatrics in Review”
7 citations,
November 2013 in “Pediatrics in Review” Acne is a chronic skin condition not caused by poor hygiene or diet, and it requires long-term treatment and patient education.
 116 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
116 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Adult female acne treatment should be personalized, considering individual preferences and pregnancy, using various topical and oral medications while managing side effects and resistance.

research Acne
231 citations,
April 2005 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Acne affects most teenagers and can continue into adulthood, with various treatments available that show improvement but have concerns like antibiotic resistance and side effects.
 January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” The document explains various skin conditions and their treatments.
 98 citations,
May 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
98 citations,
May 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” There are many treatments for permanent hair loss disorders, but their effectiveness varies and there's no clear best option.
 1 citations,
January 2010 in “Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology”
1 citations,
January 2010 in “Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology” The document concludes that effective acne treatment requires a personalized combination of therapies and long-term commitment, with retinoids being important for maintenance.
 76 citations,
November 2009 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
76 citations,
November 2009 in “Medical Clinics of North America” Hormones, especially androgens, play a key role in acne, which can be a symptom of systemic diseases like PCOS and may require targeted treatment.
69 citations,
March 2016 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Topical retinoids effectively improve photodamaged skin.
 151 citations,
May 2014 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
151 citations,
May 2014 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Effective treatments for male pattern baldness include oral finasteride and topical minoxidil, while topical minoxidil is best for female pattern baldness.
 118 citations,
April 1998 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
118 citations,
April 1998 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Finasteride and minoxidil are effective for hair regrowth, while treatments for alopecia areata have varying success and continuous treatment is necessary.
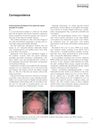 12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A woman developed a scalp condition from using minoxidil, which improved with a different treatment but left scarring.
 17 citations,
April 2006 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
17 citations,
April 2006 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Older women face various skin issues like dryness and thinning, and treatments are available but can have side effects; proper skin care and legal health decisions are important.
 August 2009 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
August 2009 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Pregnancy can cause skin changes and conditions that need correct diagnosis and treatment for the health of the mother and baby.
1 citations,
August 2024 in “Cosmetics” Melasma treatment is difficult, but combination therapies and personalized plans show promise.
10 citations,
June 2011 in “PubMed” Most skin care products are safe during pregnancy, but avoid hydroquinone and tretinoin.
 16 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
16 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Minoxidil effectively treats hair loss, especially androgenetic alopecia, but needs more research for better understanding.
 159 citations,
March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
159 citations,
March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some skin medications are safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but others can harm the baby and should be avoided.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” The document says that early treatment of Acne Vulgaris is important to prevent scarring and that adult onset acne is common in women, often due to hormonal imbalances.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
April 2023 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” Using different hair loss treatments at various times can improve results and reduce side effects for people with chronic hair loss.
 13 citations,
October 1993 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
13 citations,
October 1993 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil effectively promotes hair regrowth in younger patients with small balding areas.
 34 citations,
June 2014 in “The BMJ”
34 citations,
June 2014 in “The BMJ” Pregnancy can change skin disease severity, with some conditions improving and others worsening, and treatment should balance benefits and fetal safety.
 84 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
84 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Treatments for melanin disorders exist, but more effective options needed.
 14 citations,
January 2015 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
14 citations,
January 2015 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Acitretin significantly reduced inflammatory attacks in a woman with Naevus Comedonicus Syndrome but caused side effects.
 198 citations,
October 2011 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
198 citations,
October 2011 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Use minoxidil for hair loss; finasteride and dutasteride for men, dutasteride for women.
 120 citations,
July 2005 in “Dermatologic surgery”
120 citations,
July 2005 in “Dermatologic surgery” Niacinamide improves aging skin and is safe for use in cosmetics.
 5 citations,
March 2021 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
5 citations,
March 2021 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Biotin supplementation during isotretinoin treatment for acne may help maintain skin hydration and improve hair growth.
 47 citations,
October 2014 in “Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs”
47 citations,
October 2014 in “Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs” New alopecia treatments aim for better results and fewer side effects.
 8 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
8 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Current research explores hair growth drugs, while future research aims for personalized treatments.
 466 citations,
August 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
466 citations,
August 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Rosacea is a skin condition with unclear causes, classified into four subtypes.
 89 citations,
June 2012 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
89 citations,
June 2012 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Actinic keratosis can lead to skin cancer, is more common in fair-skinned people, and can be reduced with sunscreen and treated effectively.



























