5 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” Frontal fibrosing alopecia might be linked to autoimmune diseases.
98 citations,
March 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology” Damaging mutations in NFKB2 cause a severe and distinct form of primary immunodeficiency with early-onset and often ACTH-deficiency.
 90 citations,
December 2007 in “Current Oncology”
90 citations,
December 2007 in “Current Oncology” Non-hormonal treatments should be used first for sexual dysfunction in postmenopausal breast cancer patients on aromatase inhibitors, with hormones as a second option.
[object Object]  8 citations,
January 2018 in “Middle East Journal of Digestive Diseases”
8 citations,
January 2018 in “Middle East Journal of Digestive Diseases” A man with complete hair loss and ulcerative colitis regrew hair after treatment with azathioprine.
 3 citations,
June 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
3 citations,
June 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Dermoscopy is an effective tool for accurately detecting skin cancers.
 August 2022 in “Case reports”
August 2022 in “Case reports” Isotretinoin effectively treated a rare scalp condition, but careful drug monitoring and a dairy-free diet were important.
 January 2020 in “Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition”
January 2020 in “Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition” Low zinc levels in chronic liver disease patients are linked to more severe symptoms like taste issues and skin problems, and zinc supplements might help.
220 citations,
June 2013 in “The Journal of Pathology” Lichen planopilaris may be an autoimmune disease causing hair loss due to immune system issues in hair follicles.
 126 citations,
April 2006 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
126 citations,
April 2006 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The conclusion is that FFA and LPP have similar scalp biopsy features, making them hard to distinguish histologically, and FFA may be a specific kind of scarring hair loss.
 117 citations,
March 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
117 citations,
March 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” No effective treatment for frontal fibrosing alopecia was found, but oral 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors had the best response; for lichen planopilaris, topical corticosteroids were commonly used but had a high relapse rate.
113 citations,
May 2007 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The study found that steroids and tetracycline helped treat active Lichen planopilaris, and hair transplants were good for later stages.
 105 citations,
December 2009 in “Archives of dermatology”
105 citations,
December 2009 in “Archives of dermatology” A specific drug can help treat Lichen Planopilaris, a condition causing permanent hair loss.
 94 citations,
October 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
94 citations,
October 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Lichen planus pigmentosus causes dark skin patches and is treated by avoiding triggers and using anti-inflammatory medications.
 90 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy”
90 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy” Lichen planopilaris is a chronic, scarring hair loss condition with no definitive cure, requiring accurate diagnosis and treatment to manage symptoms.
 86 citations,
July 2012 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
86 citations,
July 2012 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” There may be a connection between Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia and Lichen Planus Pigmentosus, and more research is needed to confirm this.
 80 citations,
April 2018 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine”
80 citations,
April 2018 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine” Lichen Planopilaris and Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia may help us understand hair follicle stem cell disorders and suggest new treatments.
 79 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy”
79 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy” Oral tofacitinib can significantly improve recalcitrant lichen planopilaris.
 66 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
66 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Mycophenolate mofetil was effective for most patients in treating scarring hair loss, but some had side effects.
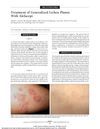 52 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology”
52 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology” Alefacept may effectively treat severe lichen planus, with patients showing significant improvement and no side effects.
48 citations,
November 2018 in “Journal of dermatological treatment” Women are more likely to have Lichen planopilaris, and treatments with cyclosporine and methotrexate are most effective but less safe than mycophenolate mofetil.
 45 citations,
February 2011 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
45 citations,
February 2011 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” People with lichen planus have higher bad cholesterol and lower good cholesterol, increasing their risk for heart disease.
[object Object] 44 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Lichen planopilaris (LPP) is linked to androgen excess, while frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) is linked to androgen deficiency.
43 citations,
March 2009 in “Archives of dermatology” No treatment showed clear superiority for lichen planopilaris.
39 citations,
November 2017 in “PubMed” Low-dose naltrexone helps reduce symptoms and slow down lichen planopilaris without side effects.
39 citations,
March 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Etanercept may cause lichen planopilaris, so doctors should be cautious.
 37 citations,
October 2015 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
37 citations,
October 2015 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Lichen planopilaris mostly affects women with fair skin and can look different on each person, needing early treatment to prevent hair loss.
37 citations,
December 2001 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Thalidomide significantly improved hair regrowth in a woman with lichen planopilaris.
35 citations,
November 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A new variant of lichen planopilaris causing diffuse hair thinning was identified.
 34 citations,
April 2008 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
34 citations,
April 2008 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Skin problems like itching, dry skin, and hair loss are more common in hepatitis C patients after interferon treatment, but lichen planus is not linked to the infection.
33 citations,
December 2014 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Lichen planus is linked to several autoimmune diseases.

















