 18 citations,
September 2003 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
18 citations,
September 2003 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” VDUP1 is found in skin and hair follicles, interacts with sciellin, and may help regulate skin cell differentiation.
 May 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
May 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” A potential treatment for atopic dermatitis could be to increase PADI1 expression to improve skin barrier function.
 12 citations,
February 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
12 citations,
February 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Combining skin tissue pathology with genetics has greatly improved the diagnosis and understanding of certain skin diseases.
10 citations,
June 2021 in “EMBO reports” When skin blisters, healing the wound is more important than growing hair, and certain stem cells mainly fix the blisters without helping hair growth.
August 2015 in “Han'gug dongmul jawon gwahag hoeji/Han-guk dongmul jawon gwahak hoeji/Journal of animal science and technology” TRα and CRABPII genes change their activity levels during goat fetal skin development.
 January 2008 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2008 in “Springer eBooks” Thyroid hormone may be useful for treating various skin conditions and needs more research.
 134 citations,
January 2011 in “Development”
134 citations,
January 2011 in “Development” Adam10 enzyme is crucial for healthy skin and proper Notch signaling.
 48 citations,
January 2015 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
48 citations,
January 2015 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Vitamin D is important for skin health and can help treat psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and vitiligo.
 28 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Thyroid Research”
28 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Thyroid Research” Thyroid hormone may speed up wound healing and hair growth, but more research is needed to understand its role in skin repair and use as a treatment.
 August 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
August 2014 in “Springer eBooks” Certain gene mutations can weaken the skin barrier and, when combined with environmental factors, lead to eczema and severe itching.
9 citations,
August 2021 in “Experimental dermatology” Hidradenitis suppurativa is a skin disease caused by the breakdown of the skin's natural immune barriers, especially around hair follicles.
93 citations,
May 2002 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Overexpressing thrombospondin-1 in mice skin prevents UVB-induced skin damage.
 9 citations,
July 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology”
9 citations,
July 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology” Topical L-thyroxine may help with wound healing and hair growth but should be used short-term due to potential risks.

Different stem cells are key for hair growth and health, and understanding their regulation could help treat hair loss.
 24 citations,
November 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
24 citations,
November 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” PPAR-γ is important for healthy hair and its problems, and more research on PPAR-γ treatments is needed.
 April 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
April 2023 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Neuropathic pruritus is a commonly overlooked and wrongly diagnosed type of chronic itching that is hard to treat.
 185 citations,
August 2005 in “Autoimmunity Reviews”
185 citations,
August 2005 in “Autoimmunity Reviews” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss due to the immune system attacking hair follicles, often influenced by genetics and stress.
 20 citations,
December 2019 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
20 citations,
December 2019 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” Blocking IL-12/IL-23 does not help with hair loss in alopecia areata for mice or humans.
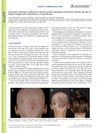 24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Tofacitinib helped a young woman's severe hair loss and arthritis but not her plaque psoriasis.
 April 2021 in “Sohag Medical Journal”
April 2021 in “Sohag Medical Journal” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, linked to genetic factors and immune system issues, with no cure yet.
 62 citations,
December 2013 in “Aaps Journal”
62 citations,
December 2013 in “Aaps Journal” Squarticles effectively deliver hair growth drugs to follicles and dermal papilla cells.
 20 citations,
November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
20 citations,
November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” IFN-γ and IL-2 are important for T cell activation in hair loss in mice.
 14 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences”
14 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences” Formulation P-08-016 better targets hair follicles for baldness treatment.
 68 citations,
May 2016 in “Experimental dermatology”
68 citations,
May 2016 in “Experimental dermatology” FFA's causes may include environmental triggers and genetic factors.
 41 citations,
February 2001 in “Current pharmaceutical design”
41 citations,
February 2001 in “Current pharmaceutical design” Current and future treatments for alopecia areata focus on immunosuppression, immunomodulation, and protecting hair follicles.
47 citations,
December 2011 in “Experimental Dermatology” CGRP may help protect hair follicles from immune system attacks, potentially slowing hair loss.
October 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking IL-12 can help treat alopecia areata by preventing hair follicle immune issues.
 May 2023 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Treg cell-based therapies might help treat hair loss from alopecia areata, but more research is needed to confirm safety and effectiveness.
 May 2023 in “Journal of Endocrinology and Reproduction”
May 2023 in “Journal of Endocrinology and Reproduction” Blocking cholesterol production may help control hair loss in Primary Cicatricial Alopecia by affecting key regulators.
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Statins may help treat alopecia areata by reducing harmful immune interactions.























