 November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology”
November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology” The document is a detailed medical reference on skin and genetic disorders.

The document concludes that diagnosing female hair loss requires careful examination, with treatments varying by condition and psychological support often necessary.

Changes in skin bacteria can affect hair loss and new treatments targeting these bacteria may prevent balding without sexual side effects.

Different scalp and hair disorders are more common in certain ethnic groups, with the most common being androgenetic alopecia, which is treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride.
November 2022 in “Frontiers in Medicine” PRP shows promise for treating mild alopecia areata but needs more research for cicatricial alopecias.
November 2022 in “Annals of Translational Medicine” Immune activities and specific genes are important in male pattern baldness.
 November 2020 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii”
November 2020 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii” Sulfotransferase SULT1A1 activity may predict minoxidil treatment success for hair loss.
 2 citations,
February 2021 in “The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology”
2 citations,
February 2021 in “The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology” Understanding the cause of bitemporal hair loss is key to deciding the right treatment.
 5 citations,
August 2018 in “PubMed”
5 citations,
August 2018 in “PubMed” An 8-year-old with severe hair loss regrew all hair after six months of tofacitinib treatment.
 November 2023 in “PubMed”
November 2023 in “PubMed” Pentoxifylline is a safe and effective alternative to triamcinolone acetonide for treating localized alopecia areata.
21 citations,
January 2021 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology” Thiopurines help treat IBD but require genetic testing to avoid side effects.
29 citations,
December 2019 in “Expert review of clinical pharmacology” JAK inhibitors are a promising new treatment for hair loss and nail problems in alopecia areata.
13 citations,
February 2017 in “Clinical rheumatology” Tofacitinib may help treat nail dystrophy, especially when other treatments fail.
 August 2023 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
August 2023 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Experts recommend personalized treatment plans for best outcomes in managing Alopecia Areata.
130 citations,
February 2019 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” JAK inhibitors are effective for treating alopecia areata, with most patients seeing hair growth after treatment.
55 citations,
October 2019 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” The review suggests that other immune cells besides CD8+ T cells may contribute to alopecia areata and that targeting regulatory cell defects could improve treatment.
14 citations,
April 2021 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Mesenchymal stem cells may help treat hair loss by improving hair cell growth and reducing inflammation.
12 citations,
July 2016 in “Journal of dermatology” Intramuscular triamcinolone acetonide is an effective treatment for severe alopecia areata, especially in males.
 3 citations,
May 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
3 citations,
May 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” A new treatment using nanoparticles can effectively prevent and reduce hair loss caused by chemotherapy.
 3 citations,
November 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
3 citations,
November 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia, a genetic disorder affecting up to 50% of adults, is caused by an excessive response to androgens leading to hair follicle shrinkage. Treatments include FDA-approved drugs, other therapies like low-dose oral minoxidil, and hair transplantation.
 November 2024 in “Skin Appendage Disorders”
November 2024 in “Skin Appendage Disorders” Misinformation about alopecia can lead to poor treatment, so it's important for healthcare professionals to correct myths.
 October 2024 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology”
October 2024 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology” Tofacitinib is a promising and safe treatment for moderate to severe alopecia areata.
 October 2024 in “JEADV Clinical Practice”
October 2024 in “JEADV Clinical Practice” UK dermatologists commonly use corticosteroids and minoxidil to treat hair loss conditions.
February 2024 in “Veterinary sciences” Canine pemphigus foliaceus involves significant immune activity and shares similarities with human pemphigus.
 January 2024 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
January 2024 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Non-biologic immunosuppressive drugs are crucial for treating autoimmune and chronic inflammatory skin diseases.
January 2024 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”  January 2024 in “Skin appendage disorders”
January 2024 in “Skin appendage disorders” Using growth factors and microneedling shows promise for hair regrowth in Alopecia Areata, but more research is needed.
 February 2022 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology”
February 2022 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology” Tretinoin alone is more effective than combined with microdermabrasion for long-term alopecia areata treatment.
 June 2024 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
June 2024 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Misinformation about alopecia is common online and can harm patient choices.
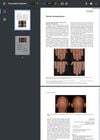 March 2024 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
March 2024 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Baricitinib improved nail condition and hair regrowth in a patient with alopecia and nail abnormalities.



















