 15 citations,
June 2018 in “Food Reviews International”
15 citations,
June 2018 in “Food Reviews International” Pumpkin seed oil may improve prostate health, bladder control, and hair growth in men.
 12 citations,
November 2020 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
12 citations,
November 2020 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Found microRNA differences in hair cells, suggesting potential treatment targets for hair loss.
 9 citations,
December 2014 in “Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment”
9 citations,
December 2014 in “Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment” People with first-time vitiligo have lower levels of a certain brain protein compared to healthy individuals.
 8 citations,
November 2015 in “Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences”
8 citations,
November 2015 in “Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences” A mix of Panax ginseng and bee-pollen may help prevent prostate enlargement in rats.
 1 citations,
January 2021
1 citations,
January 2021 CD4+ skin cells may be precursors to basal cell carcinoma.
 January 2018 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine”
January 2018 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine” ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling is crucial for skin development and stem cell function.
 January 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks” Antioxidants may help improve mitochondrial health and could be used to treat diseases related to cell damage.
 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Pubertal acne is linked to hormonal changes, affects quality of life, and is treated similarly to adult acne.
 September 1995 in “American Journal of Contact Dermatitis”
September 1995 in “American Journal of Contact Dermatitis” Antiyeast treatments work better for seborrheic dermatitis than steroids, and other findings include increased skin bacteria under plastic wrap, a nasal cell defect in Staphylococcus aureus carriers, quick resolution of certain skin reactions, high rubber latex allergy in spina bifida patients, and glyceryl monopentadecanoate's effectiveness for male hair loss.
11 citations,
February 2018 in “Oncotarget” Lower SMAD2/3 activation predicts more severe skin cancer.
161 citations,
August 2012 in “Seminars in cell & developmental biology” Hair growth and development are controlled by specific signaling pathways.
115 citations,
August 2004 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Modulating Cytochrome P450 activity could help develop new skin disease treatments.
63 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of Cellular Biochemistry” Runx1 affects hair growth, cancer development, and autoimmune diseases in epithelial tissues.
37 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” A mutation in the IKZF1 gene causes immune system overactivity, linked to autoimmune diseases like lupus.
9 citations,
August 2021 in “Experimental dermatology” Hidradenitis suppurativa is a skin disease caused by the breakdown of the skin's natural immune barriers, especially around hair follicles.
 6 citations,
May 2020 in “Nutrients”
6 citations,
May 2020 in “Nutrients” Eating fewer calories may slow skin aging and improve skin health through various biological changes.
18 citations,
July 2006 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Connexin 30 is usually absent in normal skin but can appear in certain skin conditions.
 113 citations,
December 2000 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings”
113 citations,
December 2000 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” KGF and activin are crucial for skin healing and repair.
39 citations,
November 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Fatp4 is crucial for healthy skin development and function.
 39 citations,
April 1992 in “Development”
39 citations,
April 1992 in “Development” Both cell and non-cell parts are important for rat whisker follicle regrowth.
18 citations,
June 2001 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Adding a specific gene to skin cells can help treat skin disorders like psoriasis.
13 citations,
March 1997 in “Research in Veterinary Science/Research in veterinary science” Epithelial proliferation and hyperkeratosis are linked to gastric ulcers in pigs.
37 citations,
February 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Overexpression of spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase (SSAT) in transgenic mice led to putrescine accumulation in the skin, resulting in permanent hair loss by 3 weeks of age, with hair follicles replaced by dermal cysts and epidermal utriculi. This condition mirrored hyperproliferative cutaneous disorders like psoriasis, characterized by delayed epidermal differentiation and altered expression of differentiation markers. Immunohistological analysis confirmed disturbed differentiation in SSAT transgenic skin, and similar changes were observed in organotypic cultures of transfected rat epidermal cells. Reducing putrescine levels through biosynthesis inhibition alleviated skin changes and allowed hair regrowth, indicating that keratinocyte differentiation disorders were responsible for the cutaneous changes in SSAT transgenic mice. This highlighted the importance of polyamine metabolism regulation in keratinocyte maturation.
 1 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Malassezia yeast plays a key role in dandruff and seborrhoeic dermatitis.
20 citations,
March 1990 in “Archives of Dermatology” Cyclosporine, an immunosuppressant targeting CD4+ T lymphocytes, was found to directly affect the growth of various epithelial cell types. It stimulated hair follicle keratinocytes, causing hypertrichosis, while exerting a cytostatic effect on other epithelial cells. This antiproliferative effect was also observed in some cyclosporine analogues with minimal or no immunosuppressive properties, indicating different molecular mechanisms for epithelial cell growth modulation and immunosuppression. This discovery suggested potential for using nonimmunosuppressive cyclosporines in treating hyperproliferative epidermal diseases.
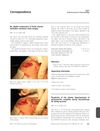 2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Chemotherapy improved a girl's painful foot condition linked to pachyonychia congenita.
August 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The study by Rahim et al. (2021) demonstrated that the balance of polyamine ratios, specifically the reduction of putrescine and increase of spermine regulated by AMD1, played a critical role in keratinocyte differentiation and epidermal homeostasis. This shift was essential for managing hyperproliferative skin disorders like psoriasis and skin cancer. The research suggested that activating AMD1 could be a promising therapeutic strategy, highlighting the importance of focusing on polyamine balance rather than total levels in treating these conditions.
 8 citations,
March 2014 in “Experimental Dermatology”
8 citations,
March 2014 in “Experimental Dermatology” Light and temperature affect the daily skin function rhythms in hairless rats, with temperature influencing water loss but not skin hydration.
 12 citations,
July 2021 in “Scientific Reports”
12 citations,
July 2021 in “Scientific Reports” Glutamic acid helps increase hair growth in mice.
 7 citations,
January 2003 in “Elsevier eBooks”
7 citations,
January 2003 in “Elsevier eBooks” Testosterone is crucial for development, growth, and various body functions in mammals.

















