 153 citations,
October 2007 in “Cell Stem Cell”
153 citations,
October 2007 in “Cell Stem Cell” New research suggests that skin cell renewal may not require a special type of cell previously thought to be essential.
 138 citations,
February 2007 in “European journal of cancer”
138 citations,
February 2007 in “European journal of cancer” EGFR inhibitors often cause skin problems and other side effects, but these are usually reversible and can be managed to keep patients comfortable.
 96 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
96 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” The document concludes that adult mammalian skin contains multiple stem cell populations with specific markers, important for understanding skin regeneration and related conditions.
 57 citations,
January 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
57 citations,
January 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” Skin stem cells maintain and repair the outer layer of skin, with some types being essential for healing wounds.
 54 citations,
January 2016 in “Cell reports”
54 citations,
January 2016 in “Cell reports” Activating β-catenin in different skin stem cells causes various types of hair growth and skin tumors.
 29 citations,
July 2014 in “PloS one”
29 citations,
July 2014 in “PloS one” Meis1 is crucial for skin health and tumor development.
 2 citations,
August 2023 in “Development”
2 citations,
August 2023 in “Development” Hair follicles in the back of the rosette fancy mouse have reversed orientations due to a gene mutation.
 1 citations,
November 2020 in “Biochemical Society transactions”
1 citations,
November 2020 in “Biochemical Society transactions” Different types of skin stem cells can change and adapt, which is important for developing new treatments.
 47 citations,
September 2015 in “Cell Cycle”
47 citations,
September 2015 in “Cell Cycle” Different skin stem cells help heal wounds, with hair follicle cells becoming more important over time.
 50 citations,
September 2014 in “Stem cell reports”
50 citations,
September 2014 in “Stem cell reports” BLIMP1 is essential for skin maintenance but not for defining sebaceous gland progenitors.
 35 citations,
October 2015 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics”
35 citations,
October 2015 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics” Tiny particles carrying roxithromycin can effectively target and deliver the drug to hair follicles without irritation.
February 2024 in “Epigenomes” Epigenetic mechanisms control skin development by regulating gene expression.
 150 citations,
April 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
150 citations,
April 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Laser hair removal effectiveness depends on targeting hair structures without harming the skin, and improvements require more research and expert collaboration.
 19 citations,
August 2012 in “Cell death and differentiation”
19 citations,
August 2012 in “Cell death and differentiation” Intu gene is crucial for hair follicle formation by helping keratinocytes differentiate through primary cilia.
 72 citations,
November 2012 in “PloS one”
72 citations,
November 2012 in “PloS one” The protein folliculin, involved in a rare disease, works with another protein to control how cells stick together and their organization, and changes in this interaction can lead to disease symptoms.
 25 citations,
September 2018 in “Molecular Biology of the Cell”
25 citations,
September 2018 in “Molecular Biology of the Cell” Blocking Wnt/β-catenin signaling with EGF receptor is necessary for proper hair growth.
 6 citations,
July 2023 in “Nature cell biology”
6 citations,
July 2023 in “Nature cell biology” SOX9 helps determine stem cell roles by interacting with DNA and proteins that control gene activity.
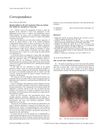 2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology”
2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology” A man's bald spot grew hair after starting cancer treatment with gefitinib.
 1 citations,
July 2023 in “Nature communications”
1 citations,
July 2023 in “Nature communications” MOF controls key genes for skin development by regulating mitochondrial and ciliary functions.
 November 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
November 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” MOF controls skin development by regulating genes for mitochondria and cilia.
 11 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
11 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Skin reactions to drugs are common and can be deadly, usually requiring stopping the drug and may be better prevented with genetic testing in the future.
 71 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of molecular cell biology/Journal of Molecular Cell Biology”
71 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of molecular cell biology/Journal of Molecular Cell Biology” mTOR signaling helps activate hair stem cells by balancing out the suppression caused by BMP during hair growth.
 51 citations,
March 2014 in “Nature Communications”
51 citations,
March 2014 in “Nature Communications” Skin tumor regression is helped by retinoic acid signaling blocking Wnt signaling.
 260 citations,
June 2011 in “Cell”
260 citations,
June 2011 in “Cell” Wnt signaling is crucial for pigmented hair regeneration by controlling stem cell activation and differentiation.
 76 citations,
June 2018 in “EMBO Reports”
76 citations,
June 2018 in “EMBO Reports” YAP and TAZ proteins are necessary for the development of two types of skin cancer.
338 citations,
April 2001 in “Current Biology” c-Myc activation in mouse skin increases sebaceous gland growth and affects hair follicle development.
48 citations,
March 2010 in “PloS one” C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta are crucial for normal skin and oil gland cell development in adult mice.
9 citations,
July 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Claudin expression changes help the skin respond to injury.
105 citations,
October 2018 in “Nature” A small group of slow-growing cells causes basal cell carcinoma to return after treatment.
 9 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology”
9 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology” A woman's ovarian tumor causing high testosterone was successfully removed, and her symptoms improved.

























