69 citations,
February 2008 in “The American journal of pathology” Controlled delivery of specific RNA and IL-4 restored hair growth in mice with autoimmune alopecia.
January 2025 in “International Journal of Biological Macromolecules” Decorin helps hair growth by influencing specific cell signals.
 41 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of experimental botany”
41 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of experimental botany” RACB in barley is crucial for cell polarity and nucleus positioning, aiding fungal infection.
 23 citations,
May 1984 in “Journal of the American Geriatrics Society”
23 citations,
May 1984 in “Journal of the American Geriatrics Society” Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia may be caused by changes in how the body processes male hormones.
2 citations,
July 2019 in “PeerJ” Removing the VDR gene in skin cells reduces their growth and affects hair-related genes.
 7 citations,
August 2022 in “Journal of Nanobiotechnology”
7 citations,
August 2022 in “Journal of Nanobiotechnology” Advancements in nanoformulations for CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing can respond to specific triggers for controlled gene editing, showing promise in treating incurable diseases, but challenges like precision and system design complexity still need to be addressed.
 271 citations,
May 2019 in “Cells”
271 citations,
May 2019 in “Cells” The secretome from mesenchymal stem cells is a promising treatment that may repair tissue and avoid side effects of stem cell transplantation.
 February 2024 in “Journal of Robotic Surgery”
February 2024 in “Journal of Robotic Surgery” The document concludes that surgical robots improve surgery and recovery but are costly and can stress surgeons due to less patient contact.
 4 citations,
June 2019 in “Revista brasileira de ginecologia e obstetrícia”
4 citations,
June 2019 in “Revista brasileira de ginecologia e obstetrícia” Using only hyperandrogenism to diagnose PCOS can lead to overdiagnosis.
 3 citations,
May 2022 in “Oncogene”
3 citations,
May 2022 in “Oncogene” Vav2 and Vav3 proteins help control skin stem cell numbers and activity in both healthy and cancerous cells.
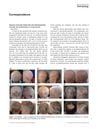 1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A 6-year-old girl with alopecia universalis regrew most of her hair after treatment with simvastatin/ezetimibe, minoxidil, and prednisolone.
 10 citations,
January 2013 in “Clinical and developmental immunology/Clinical & developmental immunology”
10 citations,
January 2013 in “Clinical and developmental immunology/Clinical & developmental immunology” The document concludes that systemic autoimmune diseases are complex, incurable, and require ongoing treatment and research.
 12 citations,
March 2011 in “Journal of pathology”
12 citations,
March 2011 in “Journal of pathology” Oncogenic K-ras causes rapid cancerous changes in the mouth's lining.
 March 2022 in “Indian Journal of Animal Research”
March 2022 in “Indian Journal of Animal Research” Dog hair follicle stem cells can turn into fat cells.
 101 citations,
January 1997 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
101 citations,
January 1997 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Nerves and chemicals in the body can affect hair growth and loss.
25 citations,
July 2016 in “Molecular biology of the cell” A protein in plants needs to bind two lipids to help with root hair growth, and this process is similar across different plant species.
 21 citations,
January 2022 in “Biomaterials Science”
21 citations,
January 2022 in “Biomaterials Science” RNA delivery is best for in-body use, while RNP delivery is good for outside-body use. Both methods are expected to greatly impact future treatments.
 12 citations,
September 2007 in “Wound repair and regeneration”
12 citations,
September 2007 in “Wound repair and regeneration” Smad2/3-dependent TGF-β signaling increases during wound healing.
34 citations,
February 2015 in “Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience” Zebrafish helped find new ways to prevent drug-induced hair cell death and potential treatments for hearing loss.
 50 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
50 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Estrogens generally inhibit hair growth and improve skin quality, but their exact effects on hair follicles are complex and not fully understood.
13 citations,
July 2020 in “World journal of stem cells” Vitamin D and calcium are important for skin stem cell function and wound healing.
6 citations,
November 2022 in “Antioxidants” OR2AT4 helps reduce aging and cell damage in human skin cells.
 23 citations,
January 2014 in “Molecular Therapy”
23 citations,
January 2014 in “Molecular Therapy” Applying a special DNA plasmid to the skin can make it thicker and stronger.
 22 citations,
August 2011 in “Endocrine Practice”
22 citations,
August 2011 in “Endocrine Practice” Most hirsutism cases are due to PCOS, and treatment focuses on lowering testosterone and blocking its effects.
 12 citations,
December 2009 in “Amino Acids”
12 citations,
December 2009 in “Amino Acids” Putting α-methylspermidine on mouse skin can start hair growth.
3 citations,
March 2023 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Keratin protein production in cells is controlled by a complex system that changes with cell type, health, and conditions like injury or cancer.
124 citations,
January 2012 in “Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” Endocannabinoids help control mast cell activity in human skin.
 114 citations,
January 2007 in “Drug Safety”
114 citations,
January 2007 in “Drug Safety” Some drugs can cause skin, nail, and hair problems, which are important for healthcare professionals to recognize and report.
7 citations,
June 2020 in “npj regenerative medicine” GDNF helps grow hair and heal skin wounds by acting on hair stem cells.
 24 citations,
August 2017 in “Prostaglandins & Other Lipid Mediators”
24 citations,
August 2017 in “Prostaglandins & Other Lipid Mediators” CRTH2 antagonists might be useful for treating many conditions because they play a role in immune and inflammation responses.



















