
Intermittent fasting slows hair growth by damaging hair follicle cells.
 November 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
November 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Valproic acid microemulsions improve skin delivery compared to regular solutions.
 May 2024 in “International Journal of Nanomedicine”
May 2024 in “International Journal of Nanomedicine” Biodegradable polymers can improve cannabinoid delivery but need more clinical trials.
[object Object] 
Wearing a toupee makes men seem more attractive and slightly healthier, but doesn't change how confident they appear.
 January 2024 in “Journal of lipid research”
January 2024 in “Journal of lipid research” Finasteride may lower cholesterol and slow heart disease progression.
 December 2023 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology”
December 2023 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology” The mTurq2-Col4a1 mouse model shows how the basement membrane develops in live mammals.
[object Object] December 2023 in “Pharmaceutics” The new adhesive nanoparticles are effective for delivering Minoxidil to the scalp without skin irritation.
 November 2023 in “Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal”
November 2023 in “Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal” A single robotic system can accurately harvest and implant hair grafts, showing promise for real-world use.
 November 2023 in “Journal of plant nutrition and soil science”
November 2023 in “Journal of plant nutrition and soil science” Boron deficiency in maize affects leaf boron levels and nutrient uptake differently depending on root hair presence and soil type.

Nanocarriers with plant extracts show promise for safe and effective hair growth treatment.
 September 2023 in “Pharmaceuticals”
September 2023 in “Pharmaceuticals” Tiny particles improved delivery of hair loss treatments to hair follicles, with lipid-based particles performing best.
 September 2023 in “Biomedicines”
September 2023 in “Biomedicines” Squalene may be a marker for certain types of alopecia.
 August 2023 in “European Journal of Plastic Surgery”
August 2023 in “European Journal of Plastic Surgery” 3D bioprinting is advancing in plastic and reconstructive surgery, especially for creating tissues and improving surgical planning, but faces challenges like vascularization and material development.
June 2023 in “Dermatopathology” A woman had a unique skin growth with hair follicle, oil glands, fat cells, spindle cells, and nerve fibers.
November 2019 in “BMC veterinary research” The hair loss in Belgian Blue crossbred calves was caused by a diet issue, not by disease or infection.
 4 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
4 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Compounds from certain trees used by First Nations people show potential for treating skin conditions and promoting hair growth, but more research is needed to confirm their safety and effectiveness.
 October 2001 in “WORLD SCIENTIFIC eBooks”
October 2001 in “WORLD SCIENTIFIC eBooks” Many substances, including chemicals and metals, can cause skin reactions; careful handling and identification of allergens are crucial to prevent dermatitis.
 24 citations,
April 2014 in “Oncotarget”
24 citations,
April 2014 in “Oncotarget” Minoxidil can reduce functions related to androgen receptors.
 7 citations,
November 2017 in “Cureus”
7 citations,
November 2017 in “Cureus” Ear creases might indicate heart disease risk, needing more research.
 October 2023 in “Pathology”
October 2023 in “Pathology” A woman had a rare reaction to ear piercing that caused earlobe swelling, which was best treated by removing the piercing and not re-piercing.
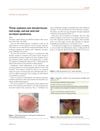 13 citations,
October 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
13 citations,
October 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The document concludes that early recognition and appropriate treatment of red scalp, red ear, and red scrotum syndromes can lead to remission.
 2 citations,
April 2017 in “Molecular Medicine Reports”
2 citations,
April 2017 in “Molecular Medicine Reports” Blocking autophagy increases survival of inner ear hair cells exposed to gentamicin.
 1 citations,
August 2023 in “Genome research”
1 citations,
August 2023 in “Genome research” The spiny mouse regenerates ear tissue asymmetrically, with gene expression differences possibly explaining its unique healing abilities.
 1 citations,
December 2021 in “Kathmandu University medical journal”
1 citations,
December 2021 in “Kathmandu University medical journal” Adult earlobe can have a benign cyst that is usually removed by surgery.
September 2024 in “Dermatology Online Journal” Facial hair growth from minoxidil stopped after she quit using it.
 September 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
September 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Increasing Rps14 helps grow more inner ear cells and repair hearing cells in baby mice.
 19 citations,
June 2008 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
19 citations,
June 2008 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” HPV genes in mice improve ear tissue healing by speeding up skin growth and repair.
 11 citations,
November 2009 in “Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research”
11 citations,
November 2009 in “Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research” Young C57BL/6 mice heal better than BALB/c mice, and older mice heal faster but regenerate worse.
 1 citations,
August 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
August 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Certain cells in the adult mouse ear come from cranial neural crest cells, but muscle and hair cells do not.

A low dose of rapamycin increases inner ear hair cell creation by boosting SOX2+ cell numbers.


























