 178 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports”
178 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing different hair and scalp diseases by their unique visual features.
56 citations,
September 2010 in “Veterinary pathology” Certain mouse strains develop a skin condition similar to a human hair loss disease due to genetic defects.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Some cosmetic procedures show promise for treating hair loss, but more research is needed to confirm their safety and effectiveness.
 October 2022 in “JAAD international”
October 2022 in “JAAD international” Most patients with autoimmune blistering diseases experienced some hair loss, which may be underreported and linked to disease severity.
 February 2024 in “International journal of biology, pharmacy and allied sciences”
February 2024 in “International journal of biology, pharmacy and allied sciences” Plant-based treatments can effectively and safely treat hair loss.
 39 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
39 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Stem cell therapy may help treat tough hair loss cases.
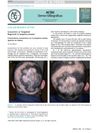 April 2016 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
April 2016 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” The document concludes that a unique target-like hair regrowth pattern in alopecia areata may be more common than thought and should be properly identified.
 23 citations,
September 2019 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
23 citations,
September 2019 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” The study concluded that AAI and DAA are forms of the same disease, with different symptoms in men and women, and that corticosteroid treatment is effective.

Dermatoscopy and videodermatoscopy are useful for diagnosing and monitoring various skin, hair, and nail conditions.
 124 citations,
August 1990 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
124 citations,
August 1990 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Diffuse alopecia in women may be related to androgens and iron deficiency, and basic hormone and nutrient screening is useful.
 103 citations,
January 2009 in “Carbon”
103 citations,
January 2009 in “Carbon” Pure carbon nanotubes are safe for mice, but impure ones cause immune issues and hair loss.
 January 2011 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2011 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia in animals can be hereditary, congenital, or acquired, with treatments and outcomes varying widely.
 99 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology”
99 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology” New treatments for Alopecia Areata show promise but need to be more effective and affordable.
 8 citations,
August 2019 in “Dermatologic surgery”
8 citations,
August 2019 in “Dermatologic surgery” Nonsteroid treatments for alopecia areata show promise but need more high-quality research.
 60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology”
60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology” Lymphocytes, especially CD8+ T cells, play a key role in causing alopecia areata, and targeting them may lead to new treatments.
 67 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
67 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease without a definitive cure, but treatments like corticosteroids are commonly used.
 January 2023 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
January 2023 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Platelet-rich plasma therapy is a safe and effective treatment for alopecia areata.
 January 2024 in “Archives of dermatological research”
January 2024 in “Archives of dermatological research” Both treatments for alopecia areata showed similar modest effectiveness.
 22 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
22 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Altered retinoid metabolism in cicatricial alopecia suggests a balanced vitamin A diet may prevent the condition.
 16 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
16 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Alopecia areata has a complex genetic basis that was not fully understood as of 2001.
 43 citations,
November 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
43 citations,
November 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” FAGA diagnosis uses blood tests and trichoscopy, with treatments like topical minoxidil, oral anti-androgens, and hormone-modulating drugs.
 May 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
May 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” 5% topical minoxidil effectively treated a boy's congenital triangular alopecia without side effects.
5 citations,
March 2016 in “Experimental and molecular pathology” Mice with alopecia areata had wider lymphatic vessels in their skin.
 8 citations,
October 2019 in “Immunological investigations”
8 citations,
October 2019 in “Immunological investigations” The AIRE gene variant rs2075876 is linked to a higher risk of alopecia areata in males.
 10 citations,
July 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
July 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Careful management of blood thinners is crucial for lupus patients with APS.
 59 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in medicine”
59 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in medicine” There are still challenges in diagnosing and treating chronic skin diseases, but there is hope for future improvements.
71 citations,
January 1998 in “Pathobiology” The document concludes that certain rats and mice are useful for studying hair loss in humans and testing treatments.
 218 citations,
January 2013 in “The Lancet Oncology”
218 citations,
January 2013 in “The Lancet Oncology” Chemotherapy causes hair loss by damaging hair follicles and stem cells, with more research needed for prevention and treatment.
 106 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
106 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The document concludes that assessing hair follicle damage due to cyclophosphamide in mice involves analyzing structural changes and suggests a scoring system for standardized evaluation.
 3 citations,
October 1993 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
3 citations,
October 1993 in “The Journal of Dermatology” The review suggests limited treatments for common hair loss conditions, with potential for future improvements.



























