12 citations,
March 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” Atopic dermatitis increases the risk of some autoimmune diseases.
 11 citations,
October 2021 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
11 citations,
October 2021 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” Hair follicle stem cells reduced hair loss and inflammation in mice with a condition similar to human alopecia.
 6 citations,
May 2023 in “Drugs”
6 citations,
May 2023 in “Drugs” Baricitinib helps regrow hair in adults with severe alopecia better than a placebo and is approved for treatment, but long-term effects are still unknown.
[object Object] 2 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology” Natural products may help treat skin inflammation from abnormal adrenal hormones.
1 citations,
May 2024 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Depression and skin autoimmune diseases are linked, needing combined care for better treatment.
1 citations,
December 2023 in “Molecules/Molecules online/Molecules annual” JAK inhibitors show promise for treating various skin diseases.
 1 citations,
April 2023 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
1 citations,
April 2023 in “Frontiers in Immunology” New treatments for hair loss from alopecia areata may include targeting immune cells, using stem cells, balancing gut bacteria, applying fatty acids, and using JAK inhibitors.
1 citations,
January 2023 in “International journal of medical science and clinical research studies” Treating stubborn hair loss involves both medical and emotional support options.
 January 2025 in “Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy”
January 2025 in “Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy” Baricitinib is effective for treating severe alopecia areata in Japanese patients, but long-term safety needs more study.
 June 2024 in “Advances in therapy”
June 2024 in “Advances in therapy” IVL3001 is safe, effective, and better than oral finasteride for treating hair loss.
April 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Alopecia areata and vitiligo share immune system dysfunction but differ in specific immune responses and affected areas.
 February 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
February 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” White hair patch repigmented and hair regrew in a balding patient after treatment with exosomes and laser.
 January 2024 in “JAAD case reports”
January 2024 in “JAAD case reports” Netherton syndrome can cause severe and chronic vulvovaginal symptoms that may improve with continuous oral contraceptives.
 September 2023 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
September 2023 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Tofacitinib is a safe and effective treatment for hair loss in children with Alopecia Areata.

Some dermatologists in Saudi Arabia prescribe Tofacitinib for hair loss, but many don't due to its unavailability and safety concerns.
 December 2022 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
December 2022 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Alopecia areata needs more recognition and better treatment access in Latin America to improve patient care and outcomes.
 September 2020 in “Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences. India”
September 2020 in “Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences. India” COVID-19 can cause skin issues like "COVID toes," rashes, hair loss, and hand eczema, and dermatologists are important for recognizing these signs.
 53 citations,
January 2018 in “JAAD case reports”
53 citations,
January 2018 in “JAAD case reports” Dupilumab for eczema may cause hair loss.
 49 citations,
December 2018 in “JAAD case reports”
49 citations,
December 2018 in “JAAD case reports” Dupilumab may cause significant hair loss, which can reverse after stopping the drug.
33 citations,
January 2019 in “Acta Dermato Venereologica” Dupilumab may help regrow hair in people with atopic dermatitis.
29 citations,
July 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Dupilumab can both heal and cause hair loss.
 26 citations,
July 2019 in “JAAD Case Reports”
26 citations,
July 2019 in “JAAD Case Reports” Dupilumab for atopic dermatitis may cause new or worsen existing alopecia areata.
19 citations,
January 2019 in “JAAD case reports” A medication for skin rash also unexpectedly treated hair loss in a patient.
 12 citations,
August 2019 in “Dermatitis”
12 citations,
August 2019 in “Dermatitis” Dupilumab for skin problems might reactivate hair loss in some patients.
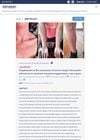 4 citations,
January 2019 in “Einstein (São Paulo)”
4 citations,
January 2019 in “Einstein (São Paulo)” Dupilumab improved severe atopic dermatitis in a patient who didn't respond to other treatments.
 3 citations,
December 2021 in “Dermatology reports”
3 citations,
December 2021 in “Dermatology reports” Dupilumab can improve both atopic dermatitis and alopecia universalis.
 2 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
2 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” JAK inhibitors are more effective and safer for treating alopecia areata than dupilumab and apremilast.
 2 citations,
June 2022 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
2 citations,
June 2022 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Dupilumab can help hair regrowth but may also trigger alopecia areata.
[object Object]  2 citations,
September 2021 in “JAAD case reports”
2 citations,
September 2021 in “JAAD case reports” Dupilumab helped a woman with severe hair loss regrow her hair quickly and maintain it for six months after stopping treatment.
 1 citations,
October 2021 in “Deleted Journal”
1 citations,
October 2021 in “Deleted Journal” Dupilumab can help regrow hair and improve skin conditions in patients with severe atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata.




















